Telemetry2U Admin Help Contents
The Administration section provides full control over users, devices, alerts, and automation settings. You can manage access permissions, set up notification groups, configure alert rules, assign nodes and gateways, and integrate external services. These tools help maintain a well-organised and efficient IoT system.
6.1 - Main Admin Page
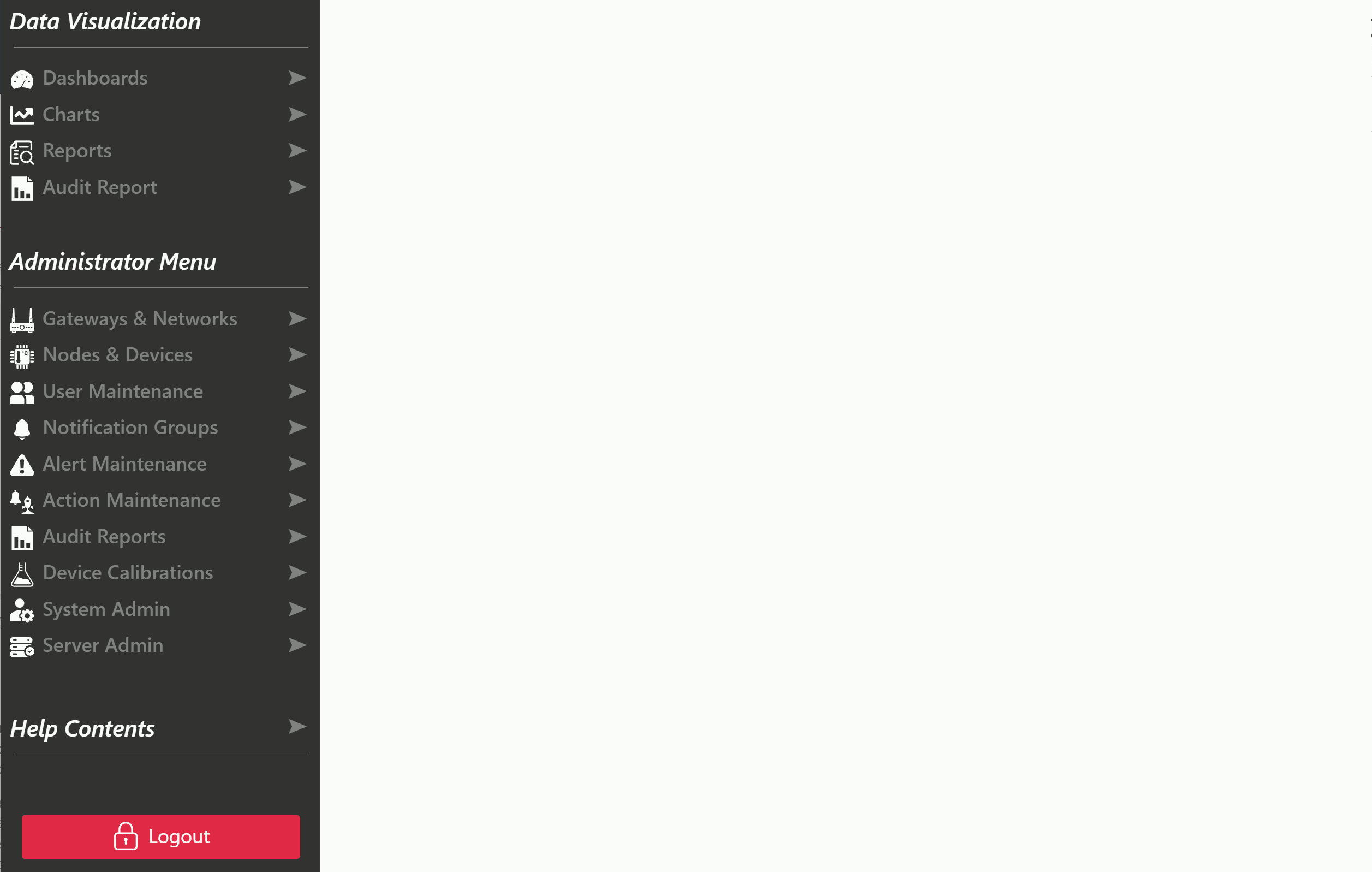
After logging in to the Telemetry2U platform, you will have access to the Side Bar on the left of the screen - If you do not see the side bar, you are not logged in to Telemetry2U. At the top of the sidebar, there is a menu icon that will open the full side menu when clicked. There are also shortcuts to all the main visualization pages and well as the administrative pages. Hover over the icons for a description.
Note:
Both the side bar and side menu will be populated depending on the user roles your account has been granted. More on this in the Understanding your Administrative Access section below.
The side menu is organized into three key categories:
- Data Visualization
- Administrator Menu
- Help Contents
Data Visualization is available to all users and provides tools for viewing real-time data on dashboards, charts, and tables, as well as generating downloadable audit reports.
Administrator Menu access is determined by the features assigned to your account. If you’ve created your own account, you will have full access to all features. However, if you were invited to join an existing account, your access may be limited based on the nodes and roles assigned to you by your administrator (the person who invited you).
Help Contents can be expanded with a click, offering quick access to support resources from any page. It should always be your first stop when seeking assistance.
Most administrative functions involve completing or editing forms. At the top of each form, you'll find notes providing additional information about what is required. You'll also notice some helpful icons on each form:
✵ - Indicates that a field is mandatory and must be completed before you can save the form.
- Indicates a Tool Tip. Hover over this icon to view more details about the field.
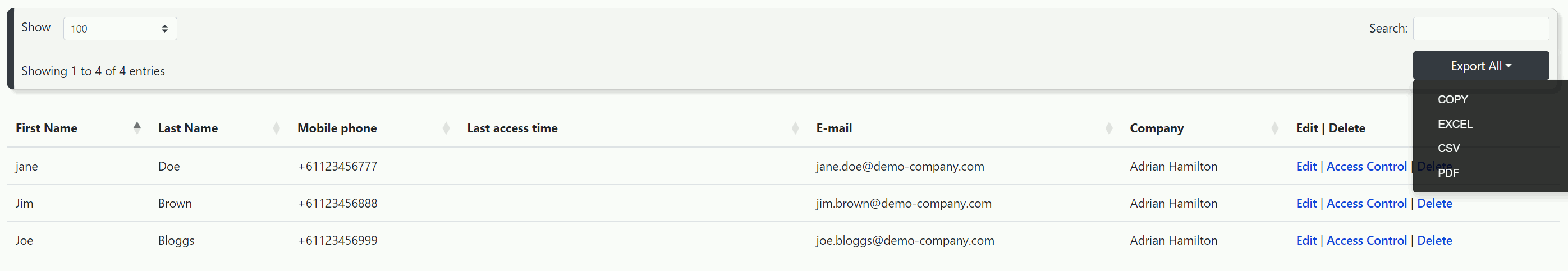
On pages where tables can contain lots of records, a filter box is available at the top of the page. You can easily sort data by columns and filter records using keywords. Additionally, you have the option to copy or export the table data in Excel, CSV, or PDF format.
Understanding Your Administrative Access
As mentioned above, each user account on Telemetry2U can be configured differently. If you created your own account with a 14-day free trial or a paid subscription, most features will be available to you. However, if you were invited to join an existing account, your access to administrative functions and node visibility may be limited depending on the User access roles assigned to you by your account owner.
Account owners have access to most features with most of the following roles assigned by default:
- Actions Admin - Create lists of downlink commands that are automatically sent to end-devices. These commands are triggered by sensor alerts or can be scheduled to run at specific times.
- Add Annotations - Add and edit annotations for alert events, which can be reviewed on the charts and reports pages. These annotations are also included in audit reports.
- Alert Admin - Create alerts for sensor inputs that can trigger notifications or actions.
- All Nodes - Grants access to all nodes under the account. Without this, users will only have access to the nodes specifically selected by the administrator.
- Audit Admin - Create and edit audit reports with customized, detailed information on sensor activity. These reports can be downloaded by all users.
- Calibration - Apply 2-point, 3-point, and offset calibrations to sensor inputs.
- Company Admin - Invite new users and manage existing user accounts, including assigning user roles and node access. Can also set up notification groups and members and manage any users dashboards.
- Confirm CRF21 Action - Telemetry2U complies with CFR21 Part 11. Users with this role can perform administrative actions by verifying their username and password when saving a form. Users without this role will not be able to perform administrative actions.
- Device Allocation - Add new or edit existing LoRaWAN and NB-IoT end-devices to the account.
- Edit Dashboard - Create and modify dashboards, which can be shared with other users in the account. Only the original dashboard creator can modify the dashboard.
- Gateway Admin - Connect and edit gateways in Telemetry2U, and set up integrations with public networks like The Things Stack and Helium.
- Node Admin - Edit node details such as descriptions and notes, but cannot modify keys essential for maintaining connection.
- View Documents - View and download documents stored with each node, including calibration and verification certificates.
- View Gateway Status - Check the online status of all LoRaWAN gateways connected to the account.
- View Raw Data - View sensor data in raw hexadecimal format on the reports page.
Account owners can assign any role to any user as needed. If a user is assigned the Company Admin role, they will also have the ability to assign roles to other users, but only the roles that have themselves been assigned by the account owner. If you you have been invited to join an existing account and require additional user access roles, you should contact your account owner directly.
Note:
The only user roles that are not available to all users (running their their own account) by default are the Calibration role and the Confirm CFR21 Action role. These features must be requested by contacting Telemetry2U.
6.2 - Company Admin
Users with the Company Admin role assigned will have access to User Maintenance section in the administrator section in the side menu. From here, all user accounts linked to the host account can be managed. This includes updating any users personal and contact details, assigning user roles, and managing node access. Company Admins can also create and manage notification groups, controlling which users are part of each group and specifying what notifications they receive and during which times. Additionally, Company Admins have the ability to manage other users' dashboards, including copying or deleting them. These functions are explained in more detail in the sections below.
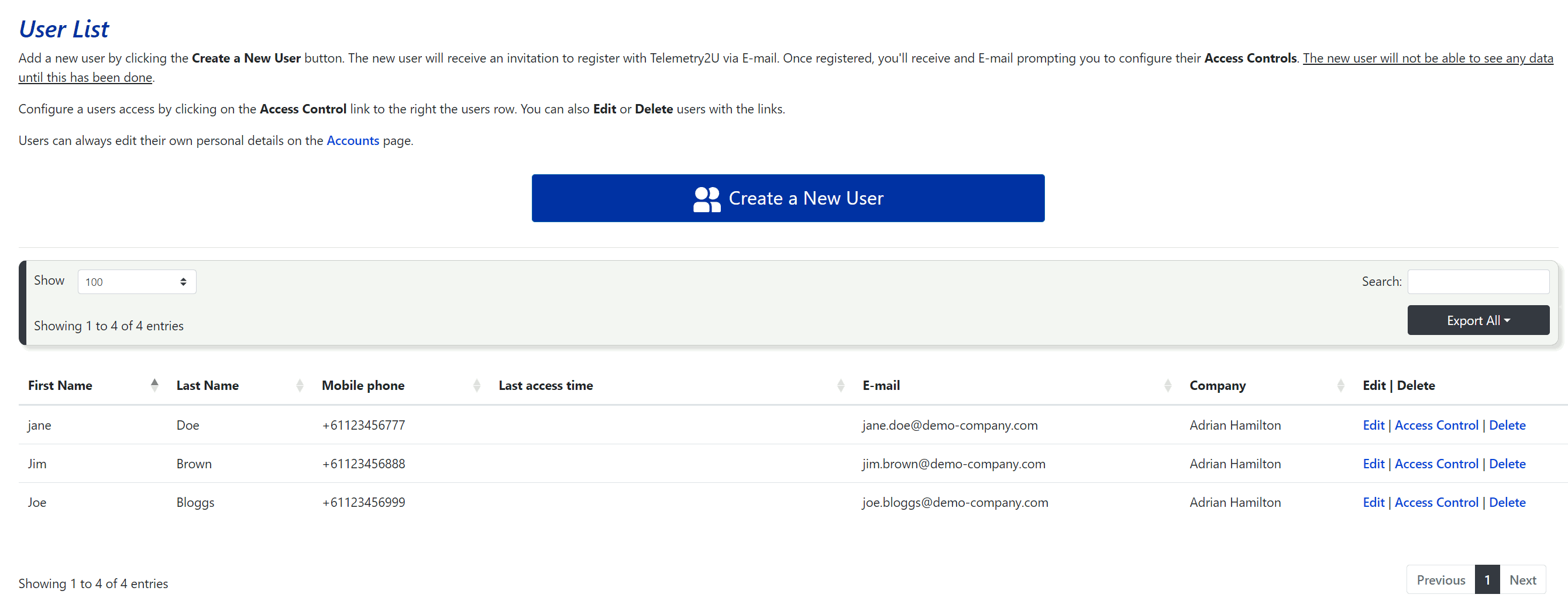
6.2.1 - User Maintenance
When you click on the Add / Edit Users link under the User Maintenance section in the side menu, you will be taken to a page displaying a table of all users linked to the host account. This table provides a quick overview of user contact details and the last time they logged in. On the right side of each user row, you’ll find options to Edit or Delete the user account, as well as configure each user’s Access Control, where you can assign specific roles and node access. The Access Control function is explained in more detail in section 6.2.3.
Note:
The forms for inviting or creating a new user and for editing an existing user are identical. The only difference is that when editing a user, the form will be pre-filled with their current details. Any field can be edited, except for the user’s login email address.
6.2.2 - Creating or Editing a User
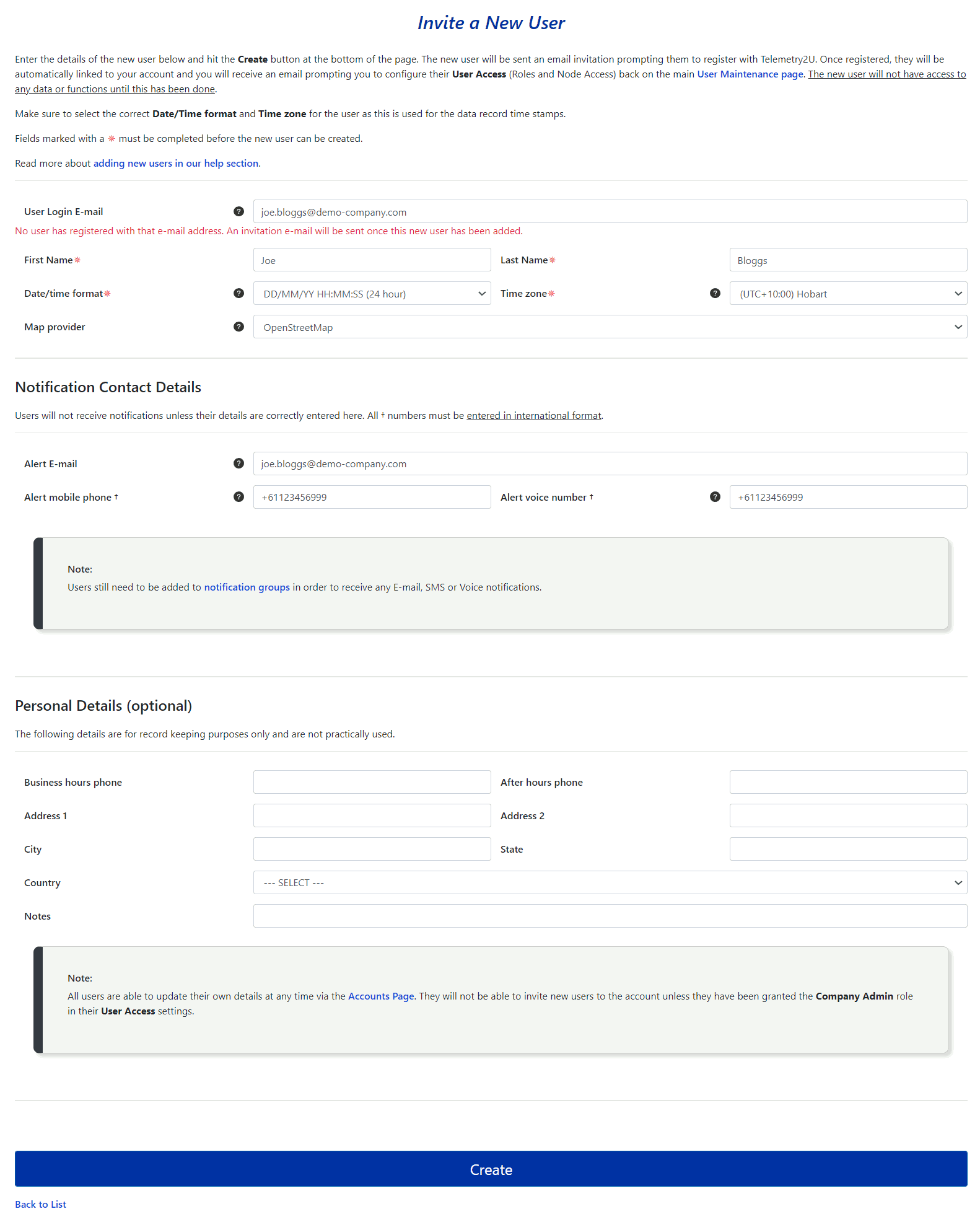
To invite a new user to join your account, click on the Create a New User button at the top of the page.
You will be taken to a new page with a form to complete. You must at least fill out the following fields:
- User Login E-mail: An E-mail invitation will be sent to this address once the from has been saved.
- First Name: The first name of the user.
- Last Name: The Last Name of the user
- Date/time Format: Sets the date and time format used on all pages.
- Time Zone: Configures the time zone for the user. This can be different than the host accounts time zone.
If the user is to receive email, SMS, or voice call notifications from alert events or if a device looses contact with the server, you will need to complete the appropriate fields in the Notification Contact Details section
- Alert E-mail: Email alerts will be sent to this address.
- Alert SMS number: SMS alerts will be sent to this phone number. It must be a mobile / cell phone number capable of receive SMS.
- Alert voice number: Voice alerts will be made to this phone number. It can be a landline or mobile number
Note:
Numbers have to be entered in international format for SMS and voice call notifications to be received reliably, e.g. +61xxxxxxxxx
The rest of the fields are optimal and can be completed a your discretion.
Once you click the Create button at the bottom of the page, the new user will be sent an email with an invitation link. This link will direct them to a page where they can Register a New Account with Telemetry2U. After they complete the registration process they will be automatically linked to your account and you will receive an email from Telemetry2U prompting you to configure the new user’s access. The new user will not have access to anything until you configure their User Controls, as explained in section 6.2.3.
Note:
It is possible to add a user to your account on their behalf. To do so, first register a new account using their email address (it does not have to be a valid email address) and generate them a password. Next, add the new user to your account using the email address just used to register the new account. Once completed, the new account will be automatically confirmed and linked to your account with no action required from the end user. You can then configure their user access settings and share the username (email address) and password with the intended user. It would be a good idea to encourage them to change their password.
6.2.3 - Configure User Access
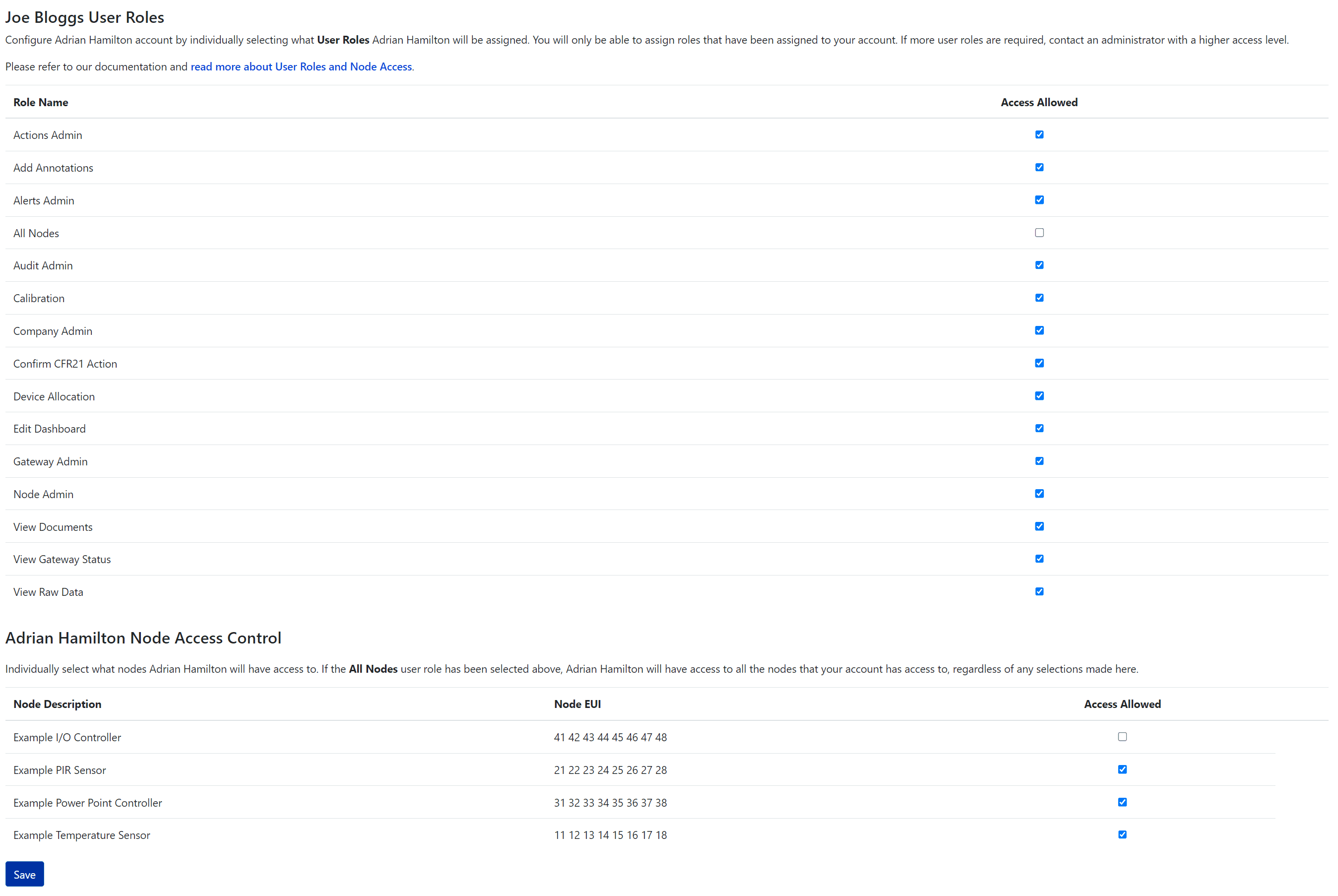
On the main User Index page, click the User Access link on the right side of any user row. This will open a new page where you can manage the user's roles and specify which nodes are accessible under their account.
As an account owner, most User Roles will be available to you, except for CFR21 Compliance and Calibrations. When you invite new users to your account, they will not have any roles or node access by default. You will need to assign roles and configure access for each user individually. Until you do this, new users will not have any access to nodes or features on the Telemetry2U platform. By default, all permissions are disabled, so you must manually grant them to each user.
Each User Role must be selected individually with the checkboxes for every user. Each User Role is described in more detail below.
Note:
You can only assign User Roles and grant access to nodes that are already assigned to your account. If you need additional roles or node access, contact your account administrator.
- Actions Admin - Create lists of downlink commands that are automatically sent to end-devices. These commands are triggered by sensor alerts or can be scheduled to run at specific times.
- Add Annotations - Add and edit annotations for alert events, which can be reviewed on the charts and reports pages. These annotations are also included in audit reports.
- Alert Admin - Create alerts for sensor inputs that can trigger notifications or actions.
- All Nodes - Grants access to all nodes under the account. Without this, users will only have access to the nodes specifically selected by the administrator.
- Audit Admin - Create and edit audit reports with customized, detailed information on sensor activity. These reports can be downloaded by all users.
- Calibration - Apply 2-point, 3-point, and offset calibrations to sensor inputs.
- Company Admin - Invite new users and manage existing user accounts, including assigning user roles and node access. Can also set up notification groups and members and manage any users dashboards.
- Confirm CRF21 Action - Telemetry2U complies with CFR21 Part 11. Users with this role can perform administrative actions by verifying their username and password when saving a form. Users without this role will not be able to perform administrative actions.
- Device Allocation - Add new or edit existing LoRaWAN and NB-IoT end-devices to the account.
- Edit Dashboard - Create and modify dashboards, which can be shared with other users in the account. Only the original dashboard creator can modify the dashboard.
- Gateway Admin - Connect and edit gateways in Telemetry2U, and set up integrations with public networks like The Things Stack and Helium.
- Node Admin - Edit node details such as descriptions and notes, but cannot modify keys essential for maintaining connection.
- View Documents - View and download documents stored with each node, including calibration and verification certificates.
- View Gateway Status - Check the online status of all LoRaWAN gateways connected to the account.
- View Raw Data - View sensor data in raw hexadecimal format on the reports page.
If you did not select the All nodes user role, you will need to manually check which nodes the user will have access to in the Node Access Control section at the bottom of the page.
6.2.4 - Notification Groups
Notification groups are made up of members (users) who can receive email, SMS, or voice call notifications from Telemetry2U. These notifications can be triggered by alert conditions or when an end-device loses contact with the server. Each user's notification settings can be individually configured within any notification group.
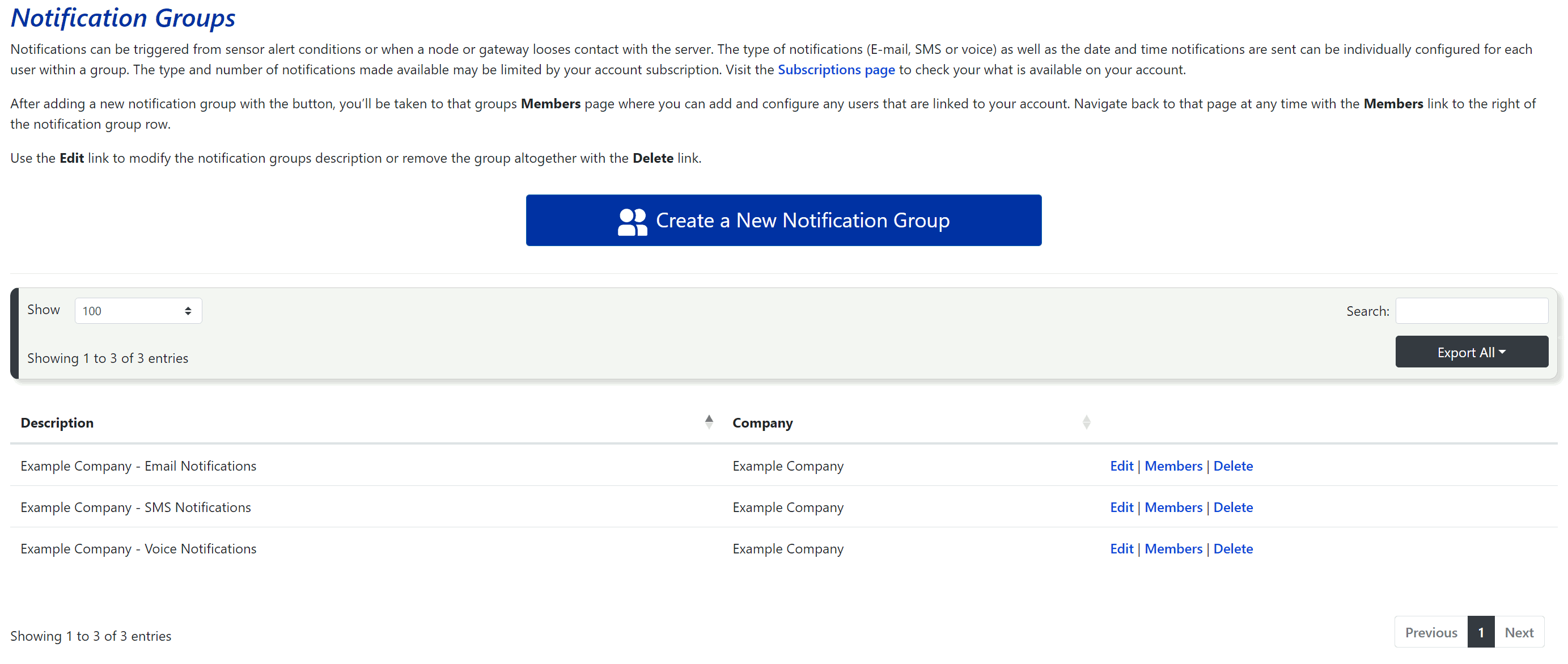
When you click on the Add / Edit Notification Groups link in the Notification Group section in the side menu, you will be taken to a page displaying a table of all notification groups currently under your account. On the right side of each row, you’ll find options to Edit or Delete notification groups, as well as a Members link, where you can add individual users to each group. The Members function is explained in more detail in section 6.2.5.
When the host account was created, three notification groups were automatically generated:
- Company Name - Email Notifications
- Company Name - SMS Notifications
- Company Name - Voice Notifications
By default, the account creator has been automatically added to each group, with the respective notification type turned on according to the group name. The time filters are configured for 24/7 notifications.
If you need additional notification groups, click the Create a New Notification Group button at the top of the page. In the new window, enter a name for the group, then click the Save button. You will be taken to a new page where you can add and configure members to the new notification group.
Notes:
We recommend creating separate notification groups for each type of notification for easier management, but you can also create a single group that triggers all notifications if preferred.
6.2.5 - Notification Group Members
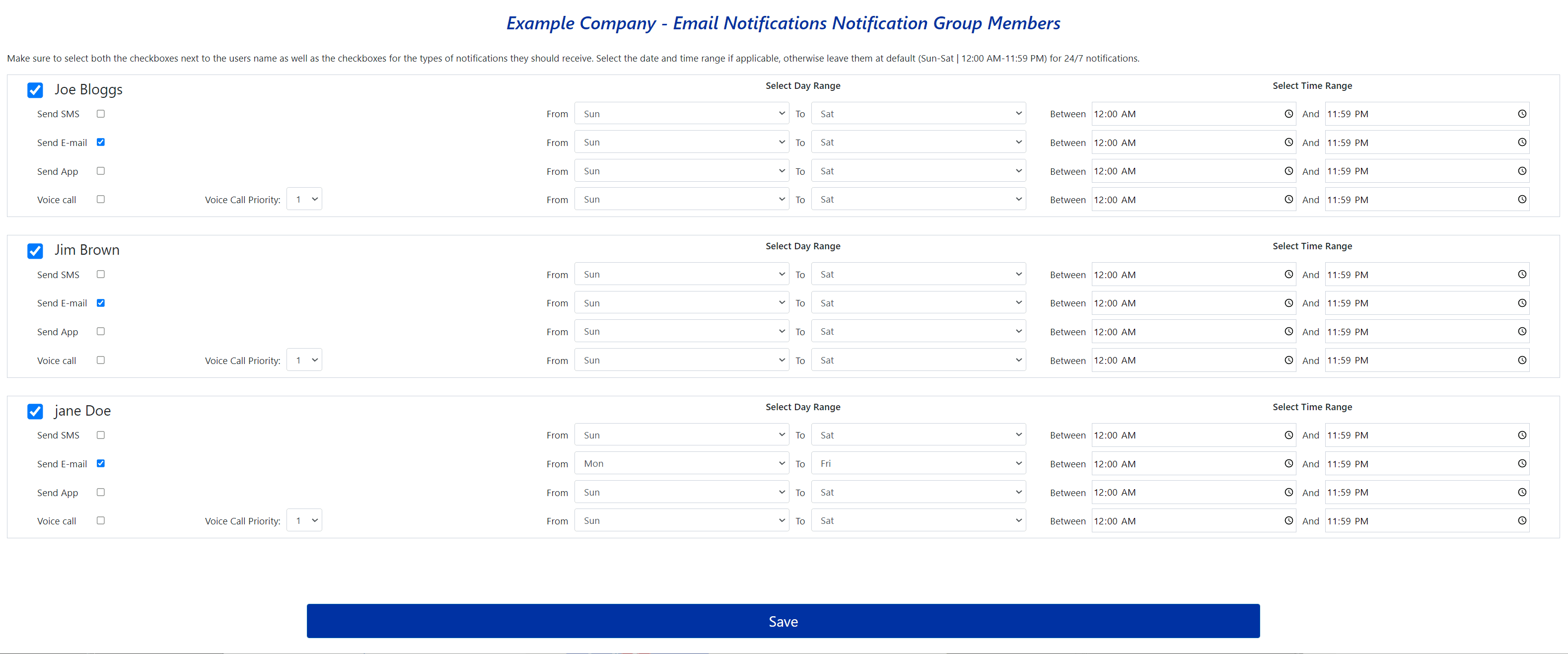
If you click on the Create New button or the Members link to the right of each notification group row, you will be taken to a page where you can configure the member settings for that notification group. Use the checkboxes to select which members should be part of the group and what types of notifications they should receive.
- Email: Emails are sent instantly, but their receipt can be delayed depending on your mail server.
- SMS: Usually received instantly, but your account must support SMS messaging.
- Voice Calls: Typically received instantly, but your account must support voice calls.
- App Notifications: Typically received instantly, but you must first install and configure the App.
You can also specify which days and times each user will receive messages for each type of notification with the date/time filter section. By default, the day/time filters are set for 24/7 - Sunday to Saturday, 12:00AM to 11:59PM
The Voice Call Priority option works exclusively with Voice Alerts. When a voice call is sent, the user will be prompted to confirm receipt via keypad input. If no input is detected, the system assumes the call was not answered and moves on to the next person on the priority list. This process repeats up to five times.
Notes:
SMS and Voice notifications will always be sent from the same phone number. It's a good idea to save +61-488-849-850 in your phone and assign it a unique ring tone so it's easily identified.
Each user must have their Notification Contact Details filled out correctly in order to receive notifications. Please refer to Section 6.2.2 for more details.
Related Links:
For a step-by-step guide on how to guide on scheduling notifications, check out TB05 - Voice call/Alert Example.
Check out our technical bulletin on installing and configuring the T2U Progressive Web App (PWA)
6.3 - Alerts Admin
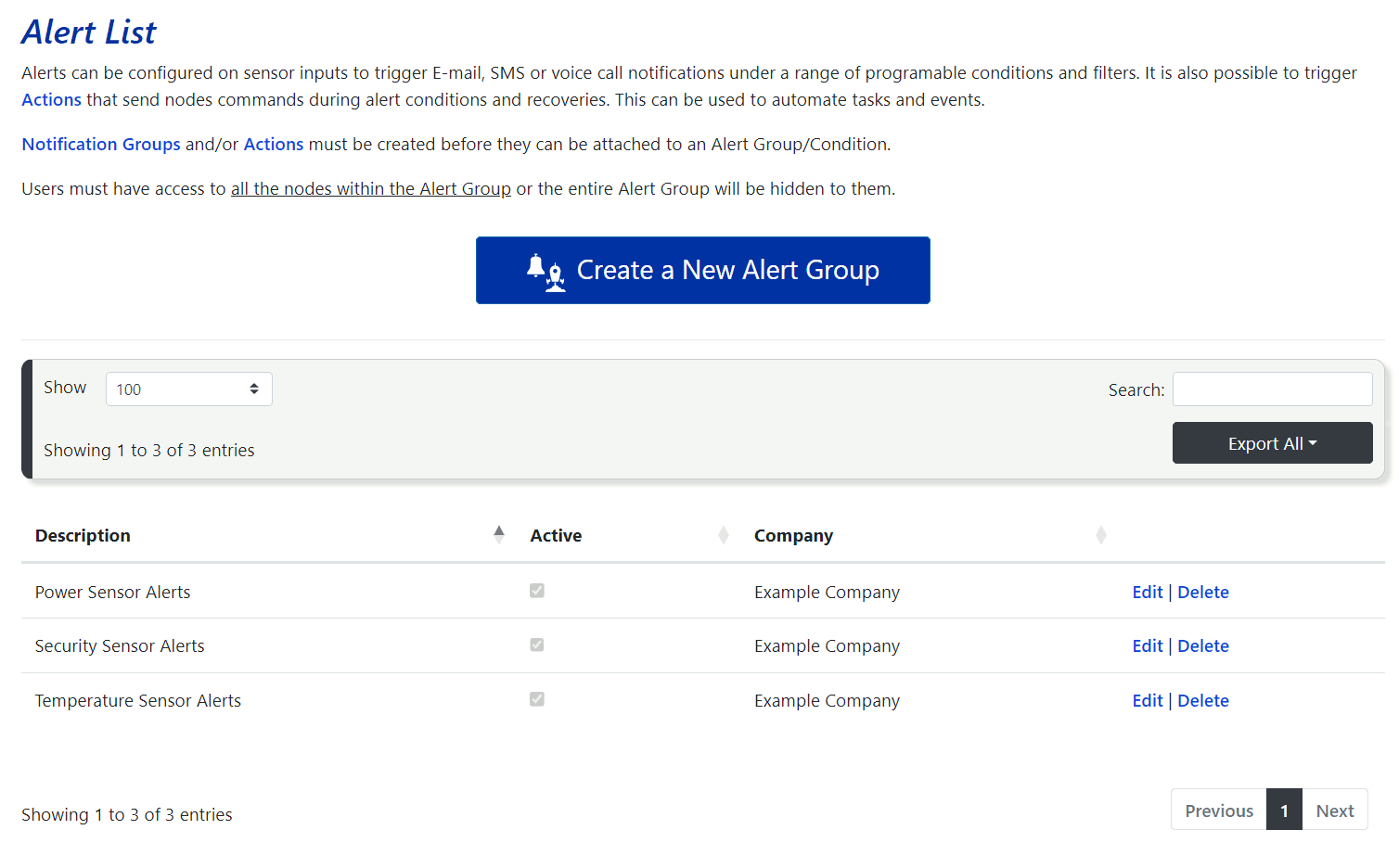
Users with the Alerts Admin role will have access to the Add / Edit Alerts and Conditions option under the Alerts Maintenance tab in the side menu. Alert groups consist of a set of alert conditions attached to individual sensor inputs for nodes linked to your account. When any alert condition is triggered, notifications are sent to all users in the notification group(s) associated with the alert group, and any configured actions will be performed. For this reason, it is important to set up your Notification Groups and Actions before configuring any alerts.
By clicking on the Add / Edit Alerts and Conditions link, you will be taken to a page displaying a table of all current alert groups associated with your account. You can quickly check the status of each group in the Active column. On the right side of each row, you’ll find options to Edit or Delete the alert group. To create a new alert group, click the Create a New Alert Group button at the top of the page. The form for creating a new alert group is the same as the one used for editing an existing alert group.
Note:
SMS and Voice notifications sent by Telemetry2U will always be sent from the same phone number. It's a good idea to save +61-488-849-850 in your phone and assign it a unique ring tone so it's easily identified.
Related Link:
Take a look at our step-by-step guide on using actions for automation - TB04 LoRaWAN IoT Automation Example.
6.3.1 - Creating and Editing Alerts
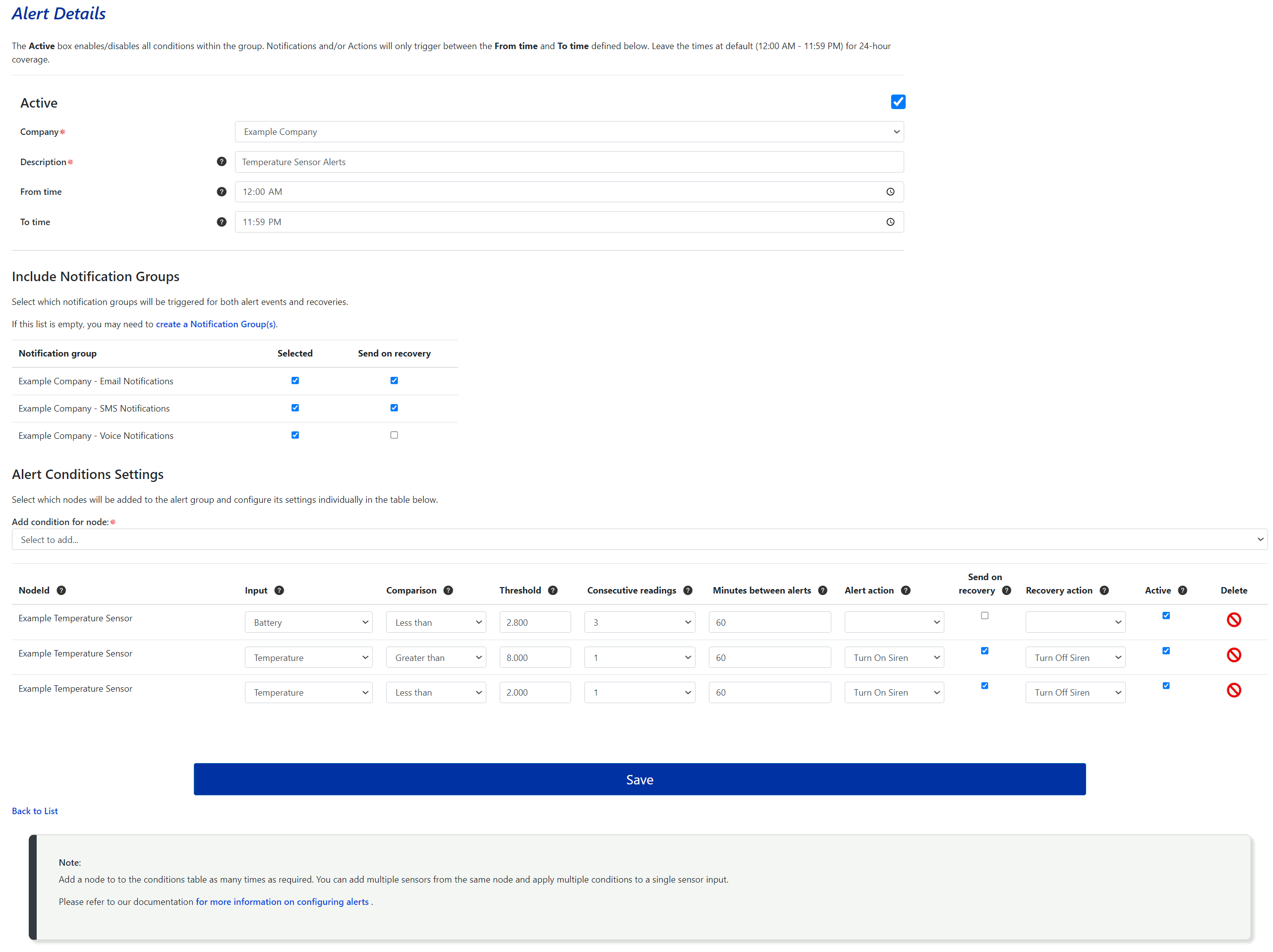
When you Create a New Alert Group or Edit an existing one, you will be taken to a new page where you can configure the alert group settings. The page is divided into three sections:
1. Alert group description and time filters. By default, alerts are set to trigger 24 hours a day (from 12:00 AM to 11:59 PM). You can manually adjust the From time and To time as needed, or click the clock icon next to each field to open a time picker. Alerts will only trigger notifications and actions within the specified time range.
2. Include Notification Groups: Select which Notification Groups should be triggered by any alert condition within the alert group using the checkboxes. If no notification groups are selected, no Email, SMS, or Voice notifications will be sent; however, any action assigned to the alert condition will still be triggered. By default, the Send on Recovery option will be checked, meaning another notification will be sent to the notification group members when the alert condition returns to a normal state.
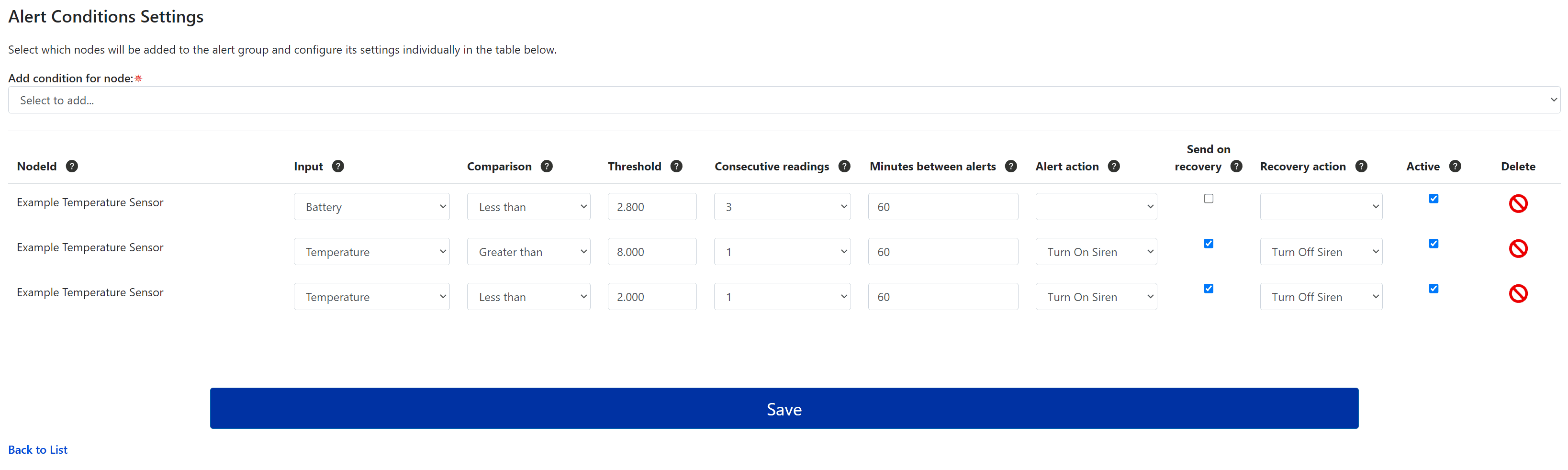
3. Alert Conditions: Alerts work by comparing the most recently received sensor value against a user defined Threshold value using various Comparison techniques. The bottom section contains a table of alert conditions that can trigger actions and send notifications to the associated notification groups. To add a new alert condition, first select a node from the Add condition for node: dropdown menu. The selected node will be added to the conditions table, where you can configure the alert condition settings and actions.
The alert condition fields and are explained further below.
- Input - Select from a list of sensor inputs available for the node that was added to the conditions table.
-
Comparison - The most recently received sensor value is compared against the threshold value with the function selected here. Choose from the following;
- Less than - Triggers if the sensor value is less than the set threshold.
- Less than or equal to - Triggers if the sensor value is less than or equal to the threshold.
- Equal to - Triggers if the sensor value is equal to the threshold.
- Greater than - Triggers if the sensor value is greater than the set threshold.
- Greater than or equal to - Triggers if the sensor value is greater than or equal to the threshold.
- Value changed - Triggers if the sensor value has changed since the previous record.
- Value not changed - Triggers if the sensor value has not changed since the previous record.
- Change below - Triggers if the sensor value has decreased below the threshold.
- Change above - Triggers if the sensor value has increased above the threshold.
- Threshold - The value that the most recent sensor input is compared to using the selected Comparison technique
- Consecutive Readings – Specifies how many consecutive 'out-of-range' readings (between 1-3) are required to trigger an alert. This functions like a delay, depending on the sensor's transmission interval. If All is selected, every out-of-range reading will trigger the alert condition.
- Minutes Between Alerts – This sets a limit on how often alerts can be sent within a specific time period. It prevents multiple alerts from being triggered if the sensor input fluctuates around the threshold value.
- Alert Action - You can select any actions that have been created from this dropdown box. The chosen action will be triggered whenever the alert condition is met.
- Send on Recovery - If this box is checked, notifications will be sent, and the Recovery Action will be triggered when the sensor value returns to its normal range.
- Recovery Action - Similar to the Alert Action described above, but this action is triggered when the alert condition recovers.
- Active - The alert condition will only trigger alerts if this box is checked. Use this to disable specific alert conditions within the group without removing them.
- Delete - Permanently removes a specific alert condition. Be cautious, as deleted alerts cannot be recovered.
Once you've finished making changes to the alert group, click the Save button at the bottom of the page. You will then be returned to the main alert page, where all your alert groups are listed.
Note:
To edit an alert group, navigate to the side menu and click Add / Edit Alert Groups. From the table that appears, find the alert group you want to modify and click the Edit link on the right-hand side.
6.4 - Node Admin
Users with the Device Allocation role will have access to the Add / Edit End Devices option under the Nodes and Devices tab in the side menu. They will have unrestricted access to add/configure as many LoRaWAN and NB-IoT devices as your account has been allocated.
Users with the Node Admin role will also have access to the Add / Edit End Devices option under the Nodes and Devices tab, but their ability to modify critical fields required for integration with Telemetry2U will be restricted. They will only be able to change non-critical information, such as the device description, device notes, and other similar fields.
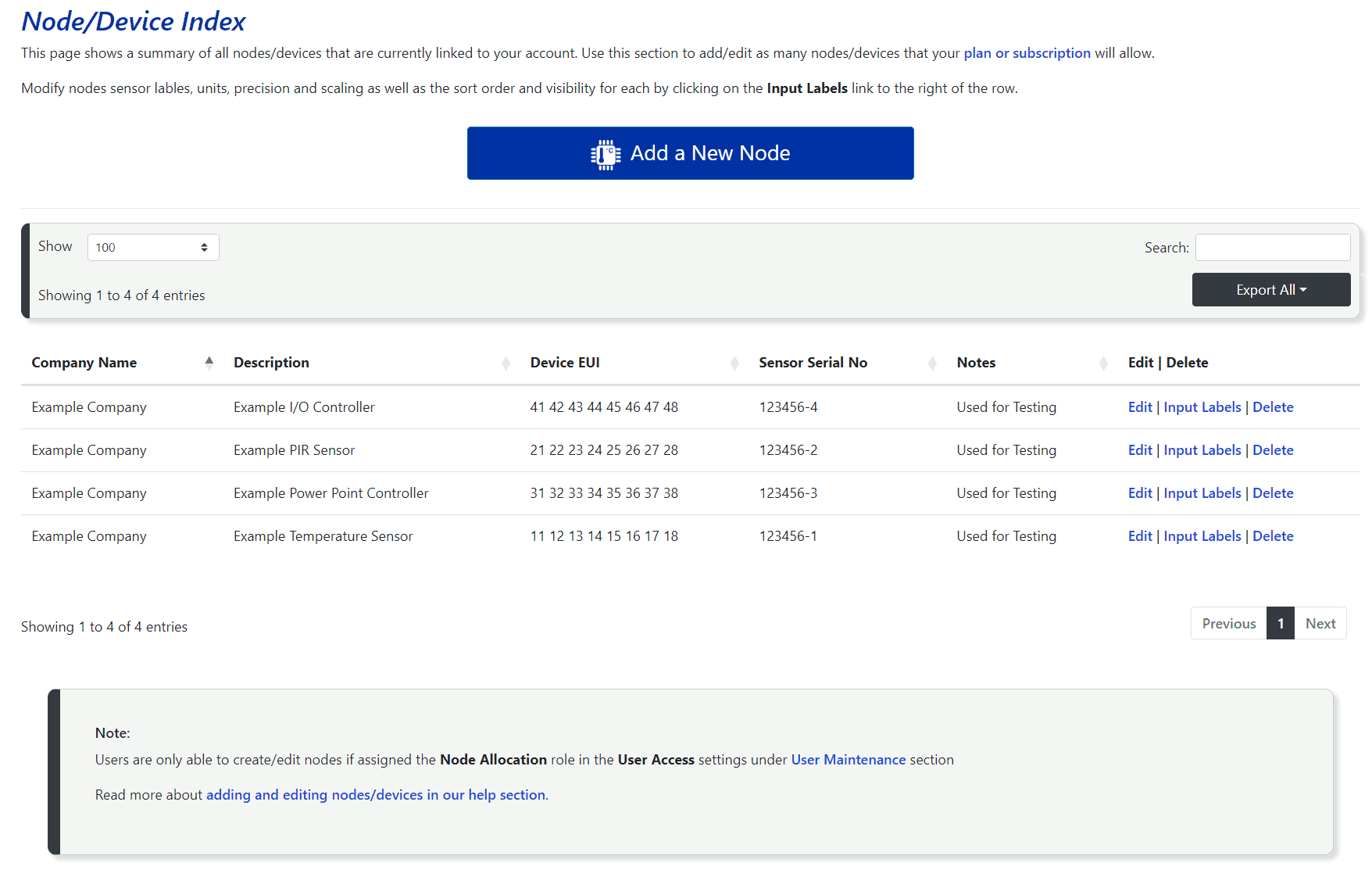
By clicking on the Add / Edit End-Devices link under the Nodes and Devices tab in the side menu, you will be taken to a page displaying a table of all LoRaWAN and NB-IoT devices currently linked to your account. On the right side of each row, you’ll find options to Edit or Delete a specific node, as well as modify the sensor Input Labels where you can rename and scale sensor inputs. This is described further in section 6.4.2 .
To add a new LoRaWAN or NB-IoT device, click the Add a New Node button at the top of the page. The form for adding a new node is the same as the one used for editing an existing node.
Note:
The number nodes/devices that can be added to your account may be limited depending on your subscription or custom plan.
6.4.2 - Creating or Editing Nodes
Before adding an end-device, ensure it is correctly configured. If you are using a LoRaWAN end-device, the frequency plan must match the LoRaWAN gateway with the gateway connected to Telemetry2U. For NB-IoT end-devices, they should already be programmed with the server address 150.101.108.130 and use UDP port 4483. If you plan to use a public network (such as Helium or TTN), make sure the integration is set up. Refer to section 6.8 for details.
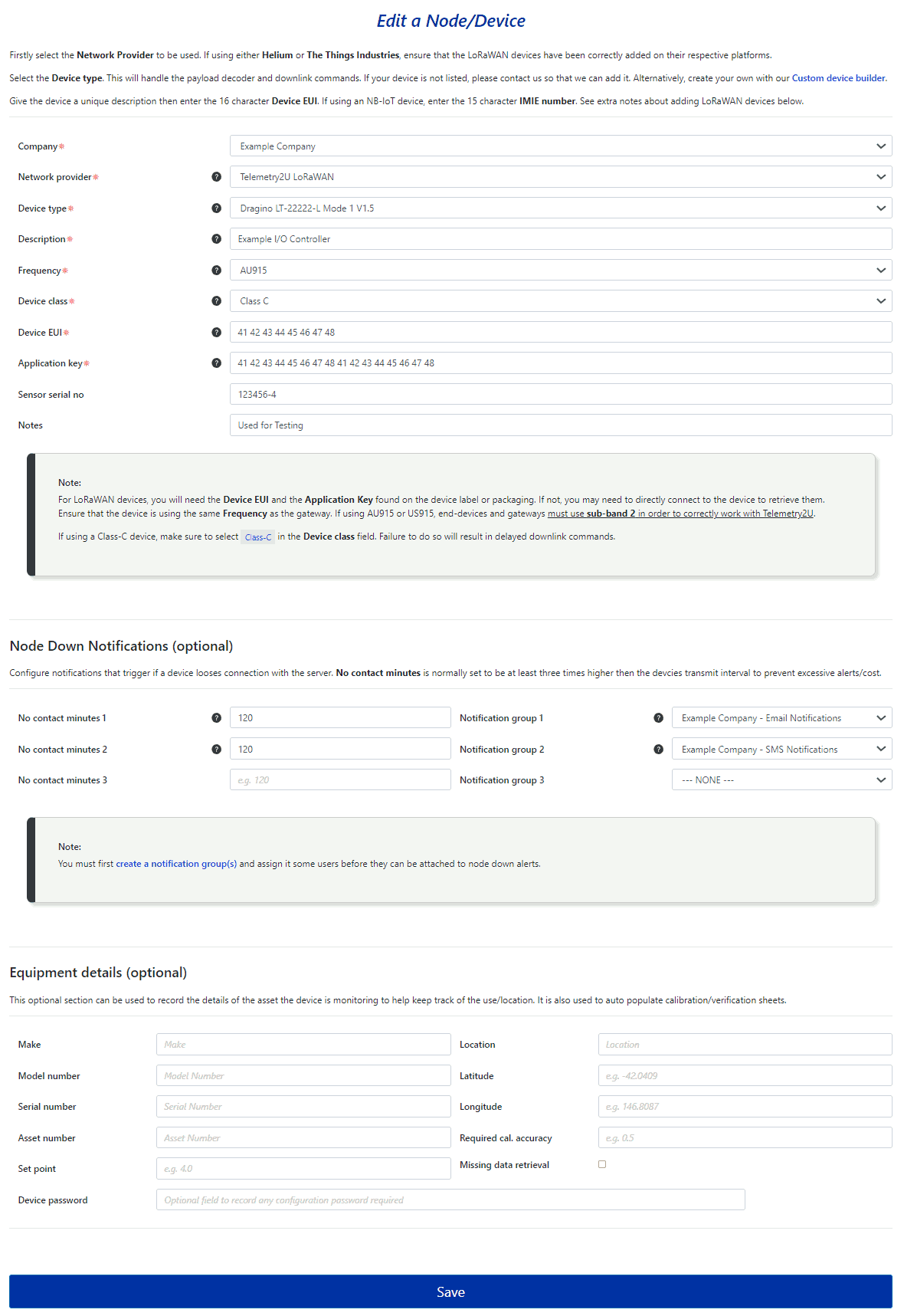
When you Add a New Node or edit an existing node, you will be taken to a new page with a form to complete. This from can be broken down in to three sections as described below. Please note that most of the device details fields are mandatory and must be completed before the page can be saved.
1. Node Details
-
Network Provider - You must choose of of the following. The choice will determine how the rest of the form is populated.
- Telemetry2U LoRaWAN - Integrate to Telemetry2U through a private LoRaWAN network. In order for this to work, you must be in range of a LoRaWAN gateway that is connected to Telemetry2U
- Telemetry2U NB-IoT over UDP - Integrate to Telemetry2U using the NB-IoT network over the UDP protocol. Your NB-IoT end-device should be programmed with the server address of 150.101.108.130 and UDP port 4483
- Helium LoRaWAN - Connect your device to Telemetry2U through the Helium network. You must first set up an integration on the Helium console. Refer to section 6.8.1 for more information
- Helium LoRaWAN - Connect your device to Telemetry2U through The Things Network. You must first set up an integration on the The Things Network console. Refer to section 6.8.2 for more information
- Device type - Sensor data is received by the Telemetry2U server in raw HEX format and needs to be converted into a user-friendly format for interpretation and display. The Device Type option configures both the payload decoder and a list of downlink commands to adjust device settings or control outputs. Telemetry2U offers several common payload decoders to choose from, or you can create your own using our simple Custom Devices page. Read more in Sections 6.4.4 – 5. Alternatively, you can contact us and request that we add the device for you.
- Description - The unique name assigned to each device, used to identify it across all pages and dashboard widgets.
- Frequency - The frequency plan that you LoRaWAN end-device is running. This must also match the gateways frequency plan.
- Device Class - LoRaWAN has three classes. You must make sure the class selected here matches your end device.
- Device EUI - For LoRaWAN end-devices, enter the 16-character Device EUI key here. For NB-IoT end-devices, enter the 15-character IMEI key.
- Application Key - Enter the 32-character Application EUI for your LoRaWAN end-device here. This does not apply to NB-IoT devices or LoRaWAN devices integrated through Helium or TTN.
- Sensor Serial No. - An optional field to store your device serial number. It is used on the calibration certificates as described in section 6.6.3.
- Notes - An optional field to store any device notes. This field is visible on the main device table.
2. Node Down Notifications
If you or any of your users would like to receive notifications when a node drops off the network for any reason, you will need to complete the Node Down Notifications section. There are two fields to fill out:
- No contact minutes – The number of minutes a node must be out of contact before a notification is triggered.
- Notification group – The notification group that will be triggered when the No contact minutes value is reached.
You can set up two different groups with individual settings. A notification will also be sent to the corresponding group when the end-device reconnects to the server.
3. Equipment Details
The Equipment Details section at the bottom of the page is optional. These fields are used to record details about the equipment that the end-device or sensor is monitoring or controlling. They are also used to automatically populate generated calibration certificates.
Click the Save button at the bottom of page after making any changes.
Note:
If the Device Type is not listed, just select any one to get started. You can then navigate to the Reports page and select Raw Data from the Report type list to see uploaded packets in raw HEX format. You can then create a Custom device as described in Sections 6.4.4 – 5. Alternatively, you can contact us and request that we add the device for you.
Related Link:
Check out our step-by-step example on how to connect a LoRaWAN device to Telemetry2U over the Helium Network.
6.4.2 - Assigning Labels to Sensor Inputs
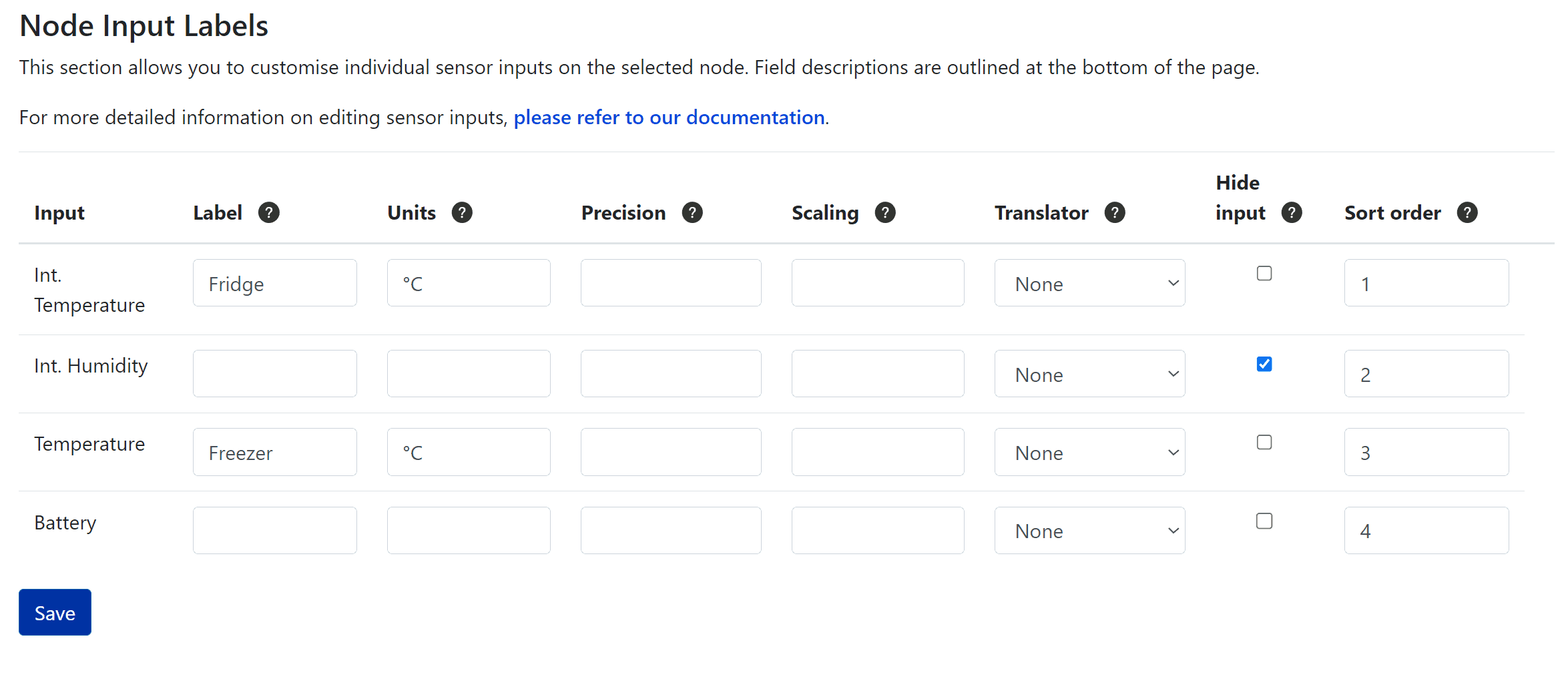
If you go back to the Node/Device Index (Nodes and Devices >> Add / Edit End Devices), and click on the Input Labels link next to a device row, you will be taken to a page where you can configure the available sensor inputs with the following settings:
- Input – Displays the individual sensors available on an end-device.
- Label – The sensor input name displayed on all pages and lists. Overrides any labels used custom decoders.
- Units – The units for the sensor input, shown on all pages and lists. Special characters and Alt-Codes are acceptable. This label overrides any units set in custom decoders.
- Precision – The number of decimal places used for the sensor input (e.g., 2 = 0.00).
- Scaling – A multiplier applied to the sensor input, used for scaling (e.g., 0.001 would convert millivolts to volts).
- Translator – For binary sensors like door or window sensors, a translator can be used to convert binary values to readable words, such as On/Off or Yes/No.
- Hide Input – When selected, the sensor input will not be visible on any pages or lists.
- Sort Order – Defines the order in which sensor inputs are displayed on charts and reports pages.
Click the Save button at the bottom of the page after making any changes. The changes will be applied immediately.
Note:
Labels allocated here with override the Description in the custom payload decoders page described in Section 6.4.4 - Creating Custom Payload Decoders.
6.4.3 - Sending Node Commands
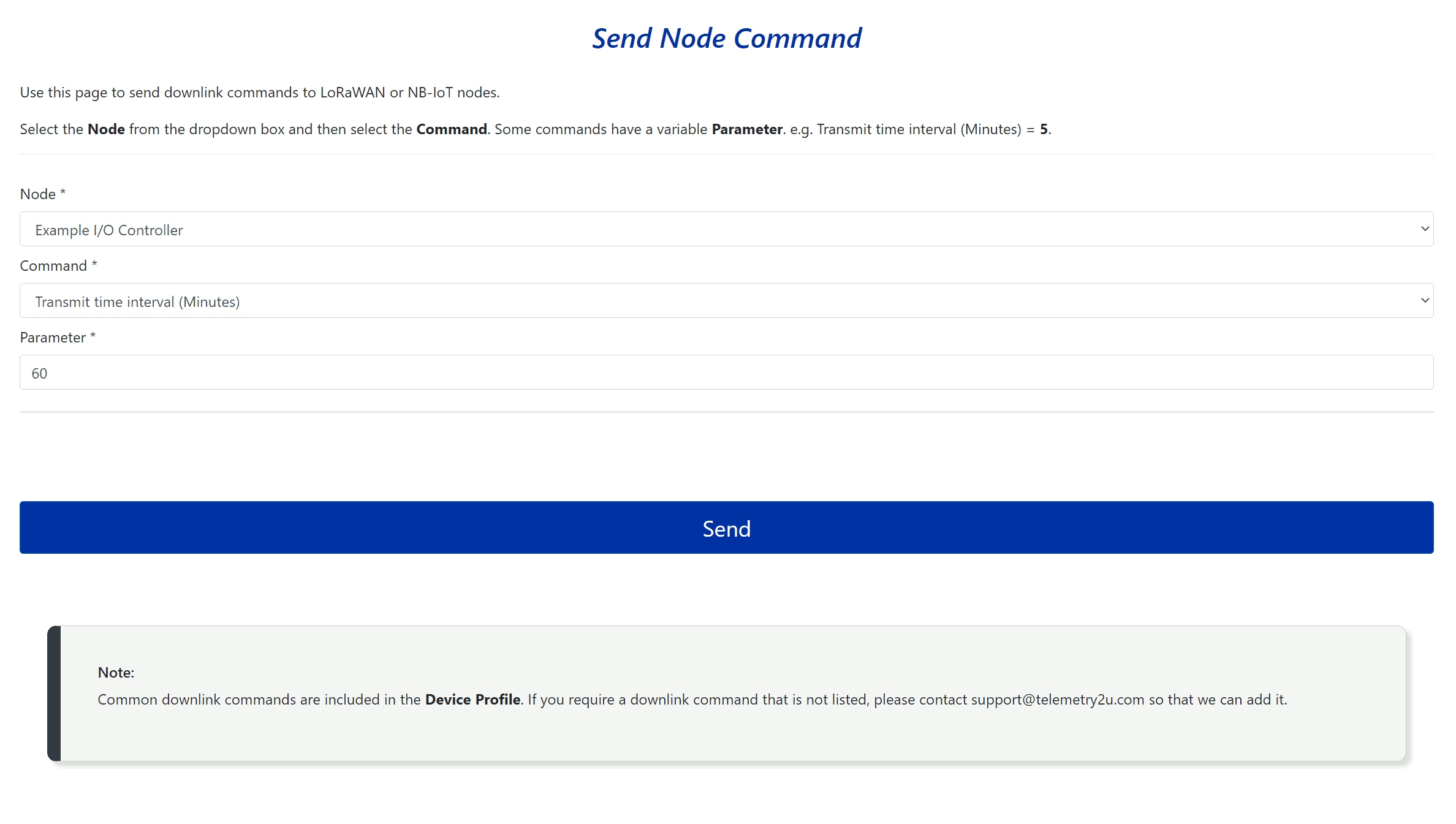
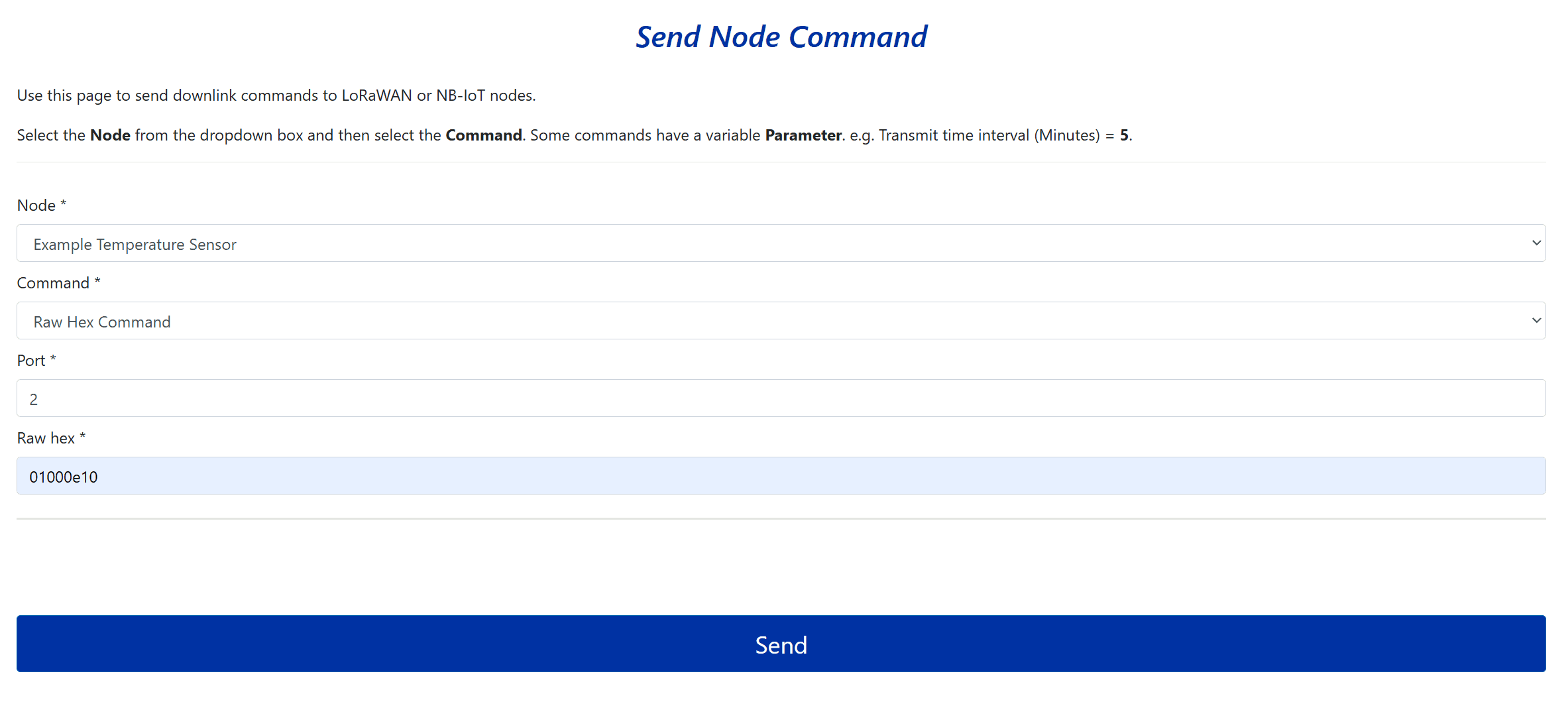
With the Node Admin role assigned, users will have access to the Send Downlink Command option under the Nodes and Devices section in the side menu. Clicking this option takes you to a page where you can send downlink commands directly to both LoRaWAN and NB-IoT devices. These commands can change device settings or control outputs. If you selected a device type when adding the device, a list of preloaded commands specific to that device will be available. If you created a custom decoder, the custom downlink commands you configured will also available. The fields are explained below:
- Node – Select the node from the dropdown list that you want to send a command to.
- Command – Choose the command you want to send to the device from the list.
- Parameter – Some commands require a variable, such as setting the transmit time (e.g., Transmit Time = 60 minutes).
The Device Class used by the end-device will determine when the node will receive the command. If Class A is used, the the node will receive the command very shortly after its next uplink. Most of the nodes used with Telemetry2U run in Class A to save power. If Class C mode was selected, the end-device would receive the command in around 5 seconds since it is awake all the time.
6.4.4 - Sending Raw Commands
As mentioned above, your selected device will have a set of downlink commands that can be sent using the method described above, however, it is also possible to send raw HEX commands to devices.
To do so, select the Raw HEX Command option from the Command dropdown box. Two new fields will appear at the bottom of the page.
- Port – This must match the device settings.
- Raw Hex – The raw hex command that will be sent to the device.
Note:
Refer to your device's user manual for a list of commands that can be sent to your specific device.
6.4.4 - Creating Custom Payload Decoders
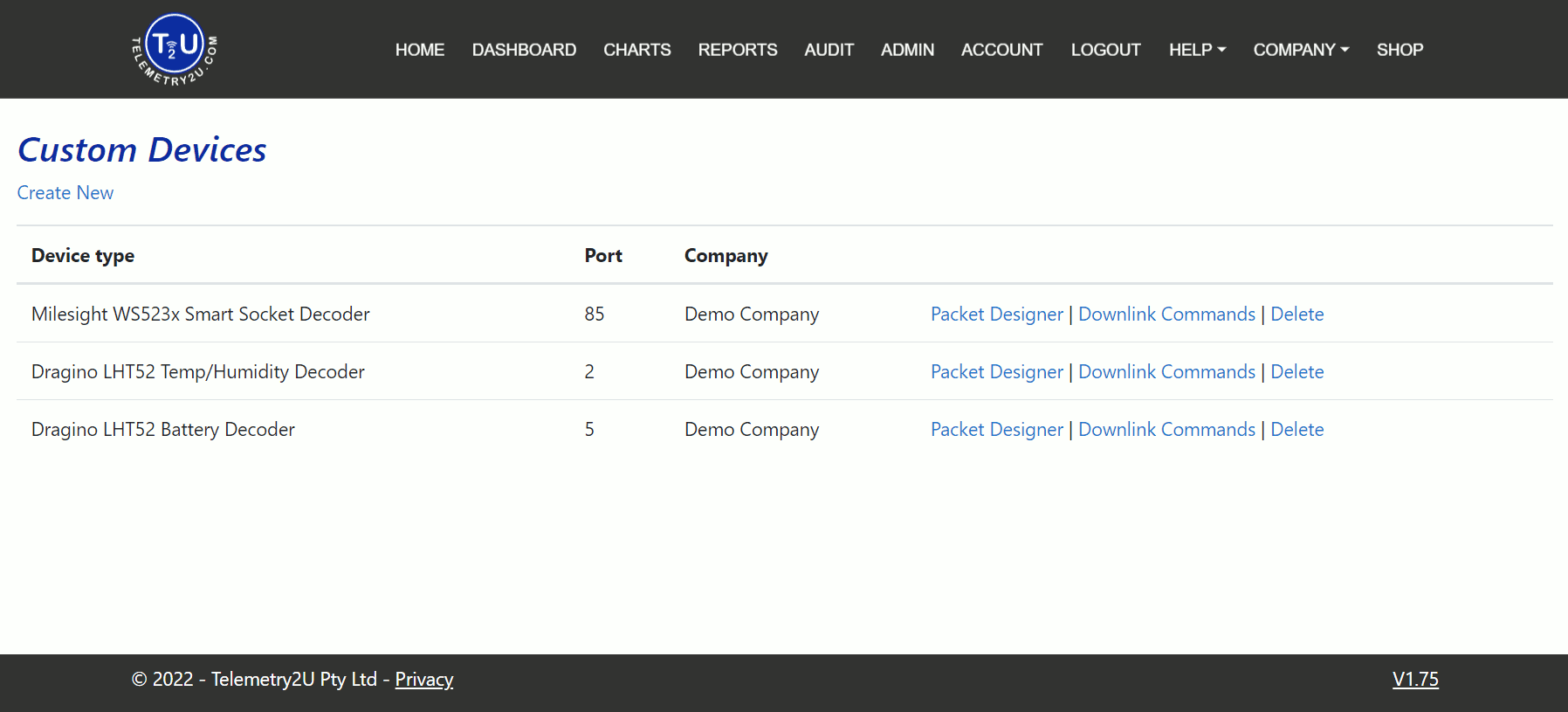
Users with the Device Allocation role will have access to the Create Custom Device Templates link under the Nodes and Devices tab in the side menu. Clicking this link will take you to the Custom Devices index page, where all custom devices are listed in a table. There are three options next to each row:
- Packet Designer – Create a custom payload decoder for the device.
- Downlink Commands – Set up downlink commands for the device.
- Delete – Remove the device.
Note:
Users with the Node Admin role assigned will not be able to create or edit custom devices.
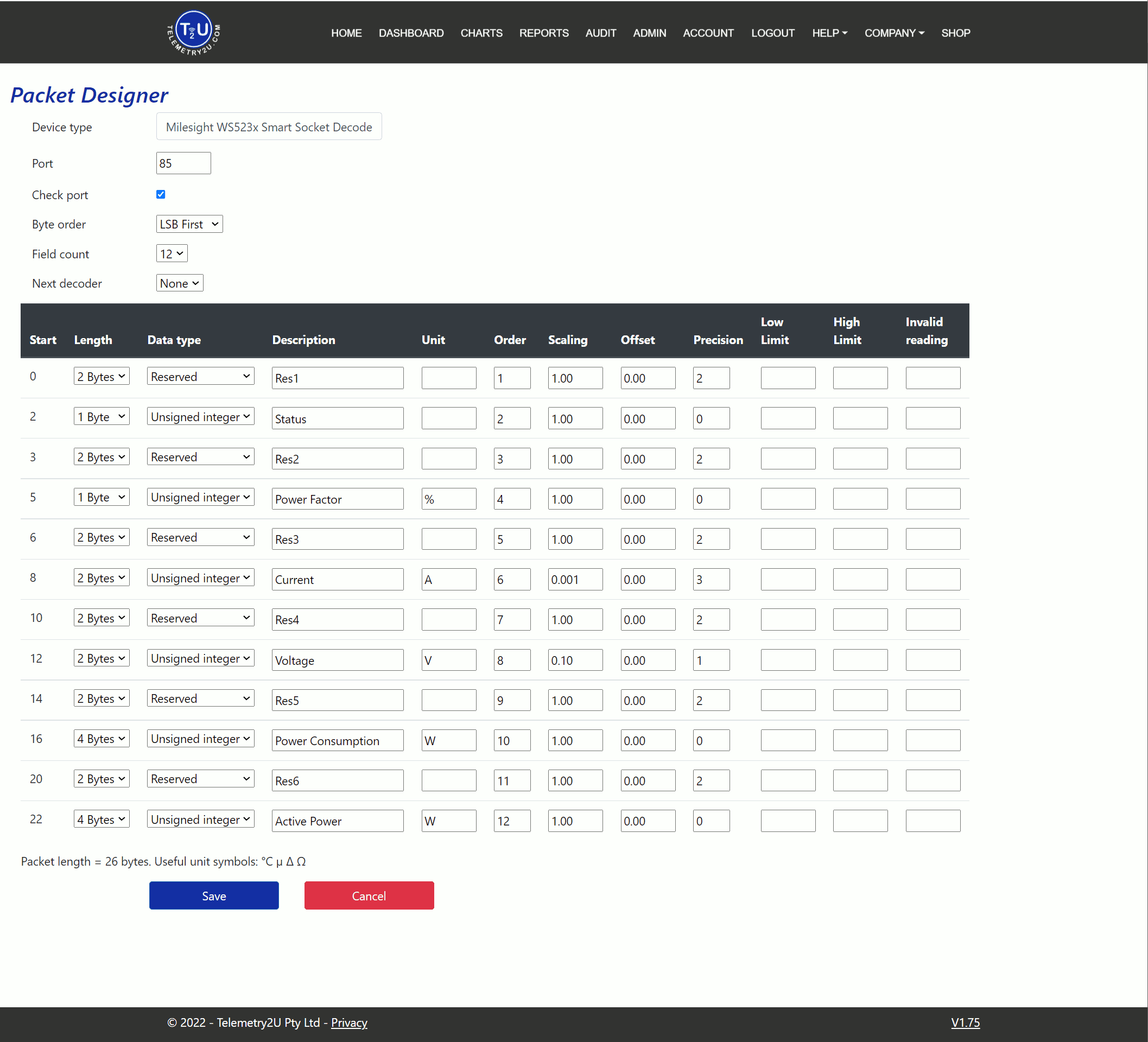
From the packet designer index page, click the Add a New Device button at the top of the page to create a new device type, or click the Packet Designer link next to any row to edit an existing device. This will open a new page where you can configure the payload designer, which is divided into two sections.
- Device Type - A unique name for the decoder, used to identify it across all pages.
- Port - Defines the port number for LoRaWAN uplinks, allowing filtering of packets by port.
- Check Port - If checked, only packets from the specified port will be processed. If unchecked, data from any port will be processed.
- Byte Order - Determines whether multi-byte fields are processed as most or least significant byte first. Refer to your device’s documentation to confirm the correct byte order.
- Field Count - Defines how many fields are in the packet, determining the number of rows in the configuration steps table.
- Next Decoder - Allows for different decoders based on the port, useful when sensors send different packets over different ports.
Note:
Telemetry2U have many Device types to select from. Before creating your own custom packet decoder, ensue that there is not already one available under the Device type option when adding or editing a node.
Once a value is entered in Field Count, the corresponding number of rows will appear in the table. Each row represents a field that the payload decoder will process. The following settings are available for each field:
- Start - Specifies the starting byte for the current row. The next row will automatically adjust based on the current row's Length.
- Length - Defines the number of bytes to process in the current row.
-
Data Type - Specifies how the data will be processed. Options include:
- Unsigned Integer - Converts the bytes into an unsigned integer (positive values only).
- Signed Integer - Converts the bytes into a signed integer (can include negative values).
- Floating Point - Converts the bytes into a floating point number.
- Match Offset - Compares the field's against the offset field. If they do not exactly match, the packet is ignored or passed to the Next Decoder if defined.
- Reserved - Skips bytes or bits that are unused or not required for reporting.
- Description - A unique name for the field, used across all pages.
- Unit - Specifies the unit for the field. You can choose from a wide range of Unicode characters.
- Order - Determines the display order of the field in charts and tables.
- Scaling - Defines a multiplier for the field value, applied before the offset, using the formula: (Reading * Scaling) + Offset.
- Offset - Adjusts the field value based on the scaling formula, unless Match Offset is used.
- Precision - Sets the number of decimal places for the field.
- Low Limit - Optionally sets a lower limit for the field. If a reading is below this value, it will be set to the low limit.
- High Limit - Optionally sets an upper limit for the field. If a reading exceeds this value, it will be set to the high limit.
- Invalid Reading - Defines a raw reading value (before scaling) that will trigger an alert if it is received. For example, some Dragino sensors report 65535 if a temperature probe is disconnected.
Click the Save button to apply your changes, or click Cancel to discard changes and exit the page.
Note:
Once you've created your custom payload decoder, it can be selected as the Device Type When you add or edit a node as described in Section 6.4.1 – Creating and Editing Nodes.
Related Link:
For some actual examples on how to create custom devices on Telemetry2U, please take a look at TB09 - Custom Payload Decoder Examples.
6.4.5 - Creating Custom Downlink Commands
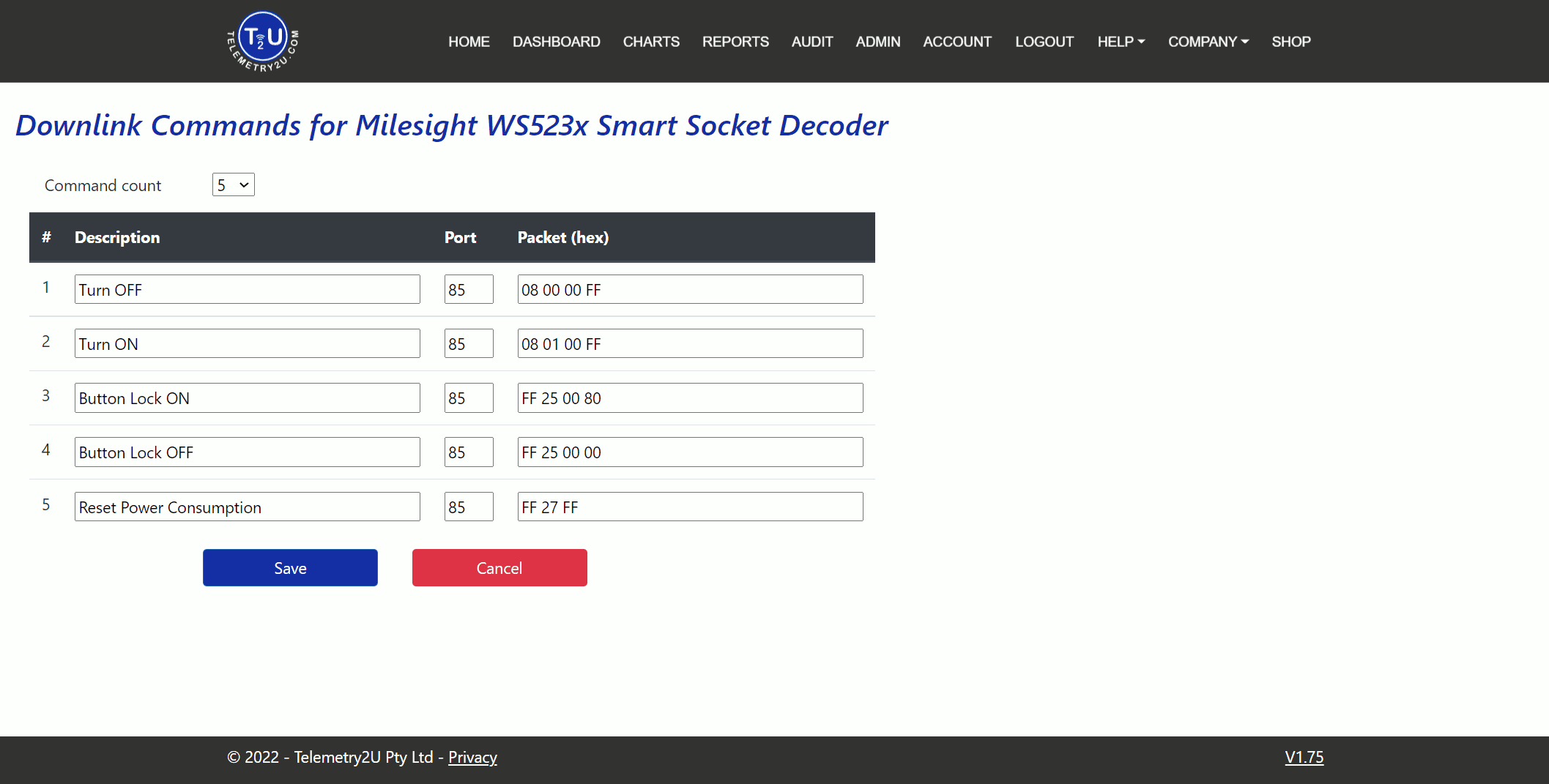
From the Packet designer index page, click the Downlink Commands link to the right of the device row. This will open a new page where you can configure the downlink commands for the device.
Firstly, select how many commands you would like to add with the Command Count dropdown box. You can add up to 20 downlink commands for each device. This will populate the table at the bottom of the page. The field descriptions are as follows:
- Description - A unique name given to the downlink command that will be used in all lists.
- Port - Commands will be sent over this port.
- Packet (hex) - The raw HEX commands to be sent to the end-device. Refer to you device user manual for a list of available commands.
Click the Save button after making any changes.
Note:
Once you’ve saved all the commands, they’ll be immediately available to send under the Send Node Command section as described in Section 6.4.3 – Sending Downlink Commands.
You’ll also be able to configure dashboard buttons with any commands as described in Section 2.2 – Building Dashboards.
6.5 - Gateway Admin
Users with the Gateway Admin role will have access to the Add / Edit LoRaWAN Gateways link under the Gateway and Network section in the side menu. Telemetry2U uses different server addresses and ports for each frequency plan. Before adding a new gateway, ensure that the Server Address, Uplink Port, and Downlink Port are correctly configured in your gateway setting. They will vary depending on your chosen frequency plan. Refer to the table below for the correct LoRaWAN gateway settings for your chosen frequency plan.
For more information on configuring your gateway, please refer to the user manual provided with your gateway.
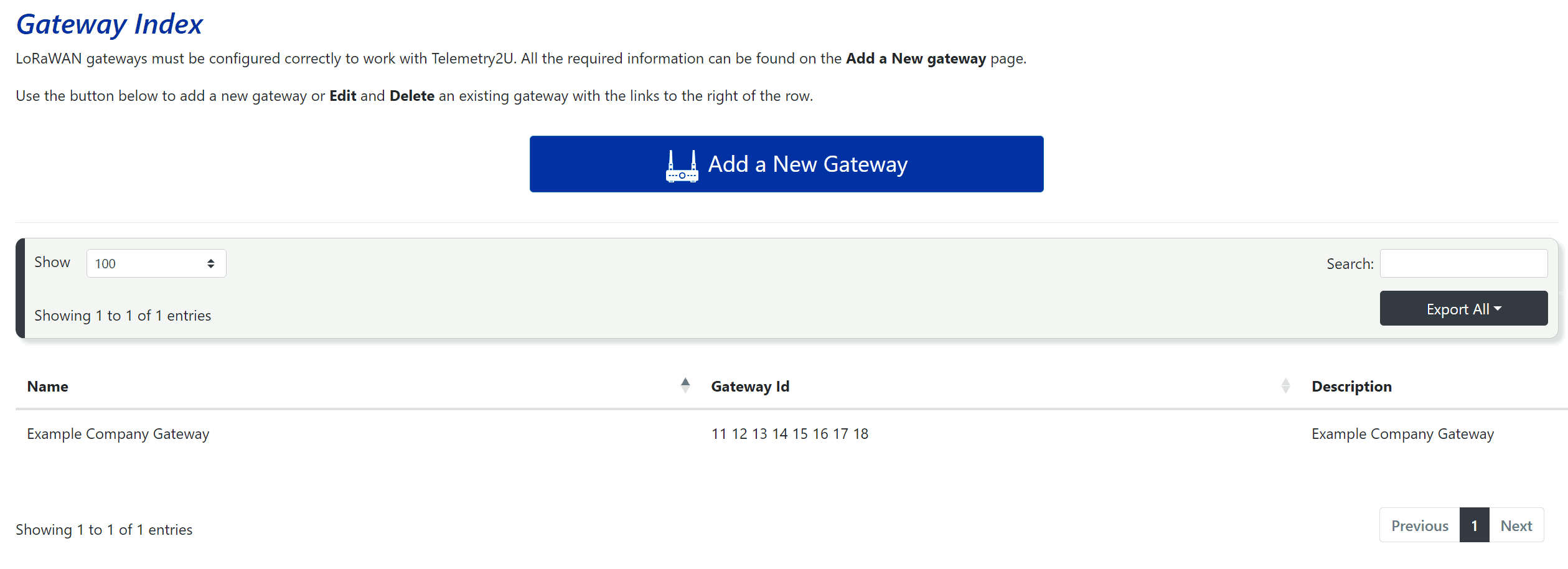
When you click on the Add / Edit LoRaWAN Gateways link, you will be taken to the Gateway index page where you can see a list of gateways that have been connected to your account. On the right side of each row, you’ll find options to Edit or Delete a specific gateway.
To add a new LoRaWAN gateway, click the Add a New Gateway button at the top of the page. The form for adding a new Gateway is the same as the one used for editing an existing gateway.
6.5.1 - Creating or Editing Gateways
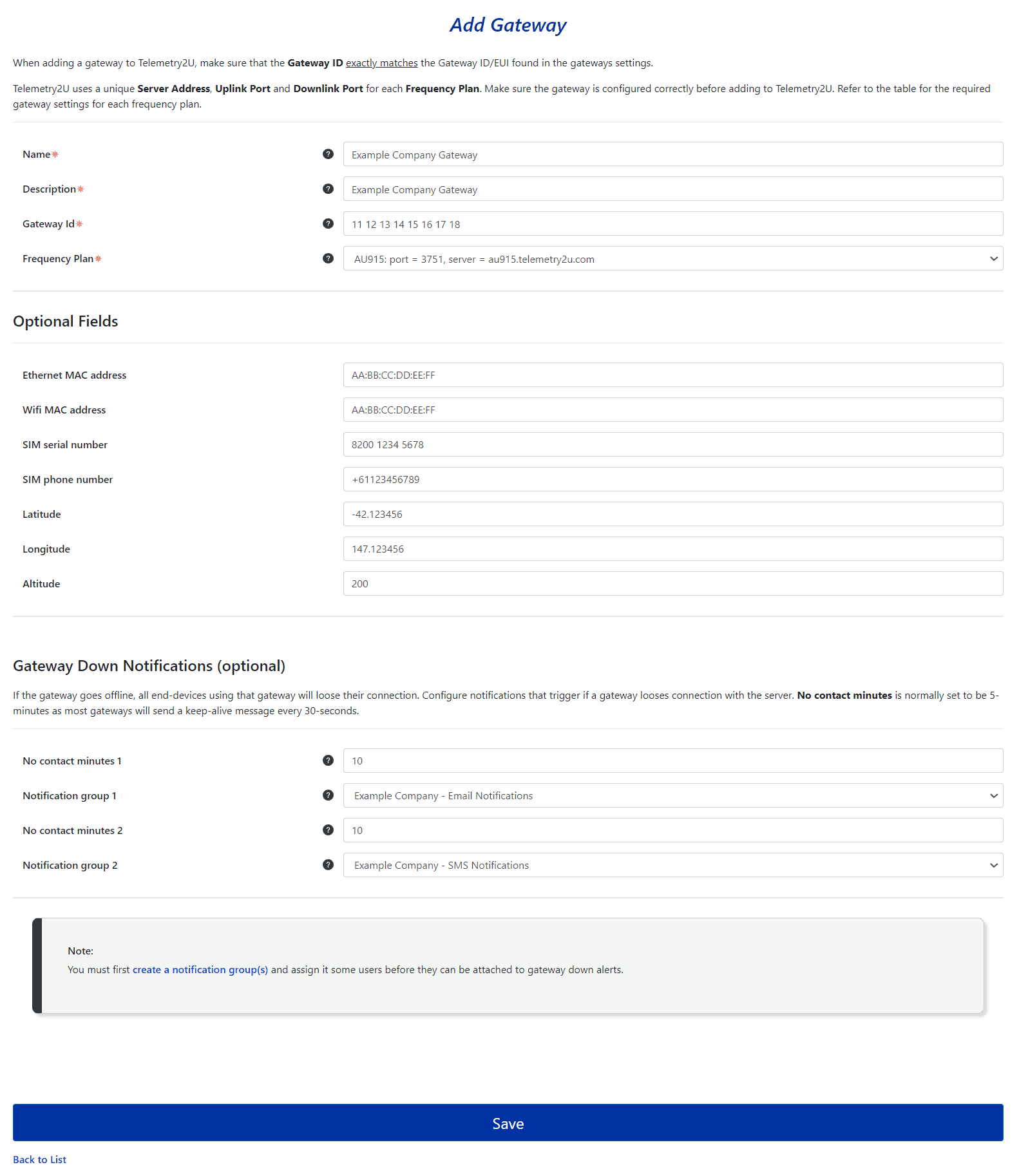
When you Add a New Gateway or edit an existing one, you will be taken to a new page with a form to complete. This form is divided into three sections, as described below. Please note that most of the Gateway Details fields are mandatory and must be completed before saving the page.
1. Gateway Details
- Name - The name given to the gateway, used to identify it on all pages.
- Description - Provide a more descriptive title for the gateway.
- Gateway ID - Every LoRaWAN gateway has a unique 16-character (8-byte HEX) Gateway ID/EUI, which must be entered here. This ID can be found in the gateway settings; refer to the gateway's user manual.
- Frequency Plan - Select the frequency plan that matches the gateway configured frequency plan. Make sure your gateway is configured with the correct server address and port for the frequency plan as defined in the table above.
2. Gateway Down Notifications
If you or any of your users would like to receive notifications when a gateway drops off the network for any reason, you will need to complete the Gateway Down Notifications section. There are two fields to complete:
- No contact minutes – The number of minutes a gateway must be out of contact with the server before a notification is triggered.
- Notification group – The notification group that will be triggered when the No contact minutes value is reached.
You can set up two different groups with individual settings. A notification will also be sent to the corresponding group when the gateway reconnects to the server.
3. Optional Fields
The Optional Fields section in the middle of the page can record additional details about the gateway. It is often a good idea to record the gateways Ethernet MAC address and Wifi MAC Address while you are connected to the gateway as these can be handy for remote management later on.
Click the Save button at the bottom of page after making any changes.
Note:
Once your gateway is successfully configured and added to Telemetry2U, you can check its connection status on the Gateway Stats page, as described in section 6.5.2.
6.5.2 - Gateway Status
Users with the View Gateway Status role will have access to the View Gateway Status link under the Gateway and Network tab in the side menu. These users cannot add or edit LoRaWAN gateways, but they can check the gateway's connection status with server.
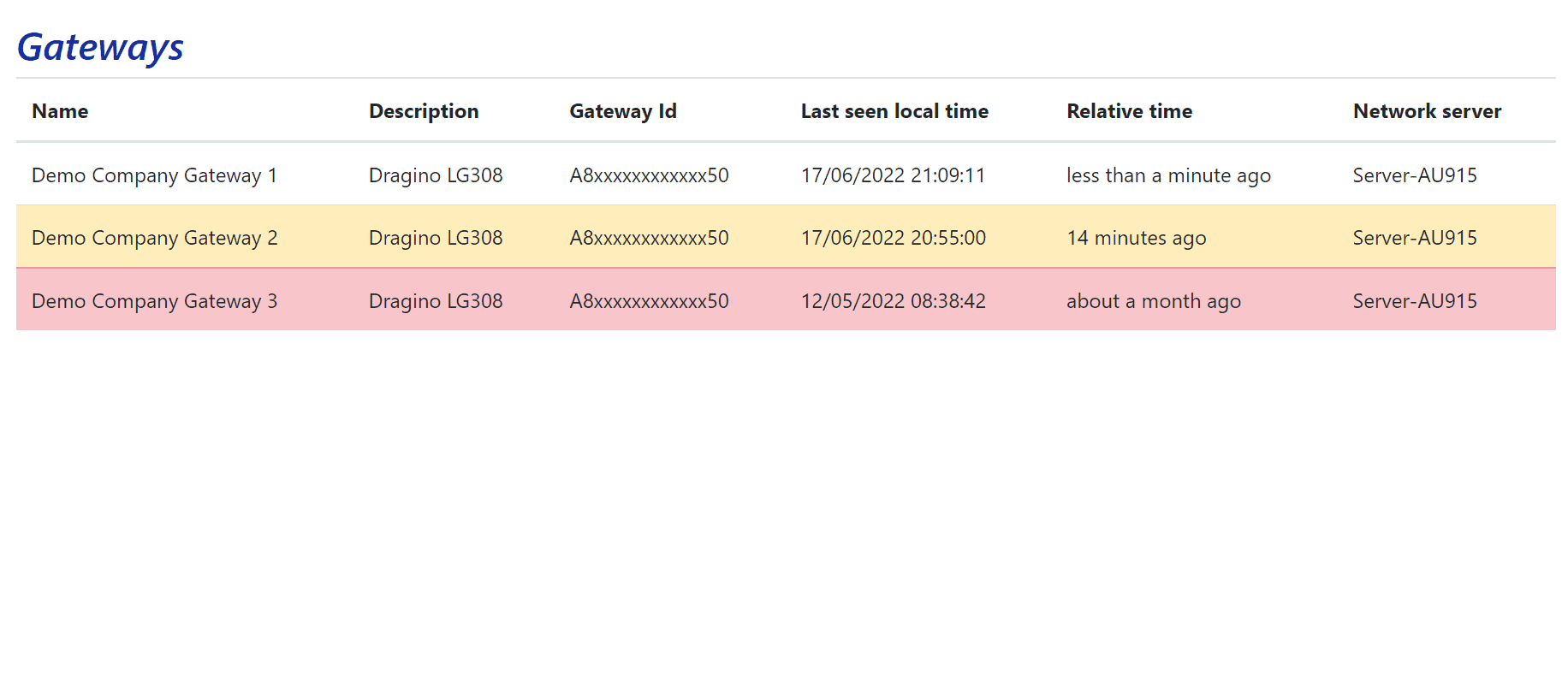
When you click on the View Gateway Status link, you will be taken to the Gateway Status index page, where you can see a list of gateways connected to your account.
The Gateway Status page uses color codes to quickly indicate the status of each gateway:
- White - The gateway has been seen within the last 10 minutes.
- Yellow - The gateway has not been seen for 10 minutes.
- Pink - The gateway has not been seen for more than an hour.
Most LoRaWAN gateways send a "Keep-Alive" message every 30 seconds, so a gateway will typically show a Relative time of less than a minute ago.
Note:
If the gateway has lost its connection, try rebooting it. If the gateway has never connected, confirm that it is configured correctly.
6.6 - Calibrations
Users with the Calibration role can access the Calibrate End-Device link under the Device Calibrations tab in the side menu. This allows users to calibrate sensor inputs using 2-point, 3-point, or offset methods. The most recently applied calibrations only affects data from midnight (00:00) on the day it's applied. Historical data remains unchanged meaning you can track sensor changes.
Note:
The calibration functions are not accessible to all account holders and must be requested from Telemetry2U directly.
6.6.1 - Entering or Editing Sensor Calibrations
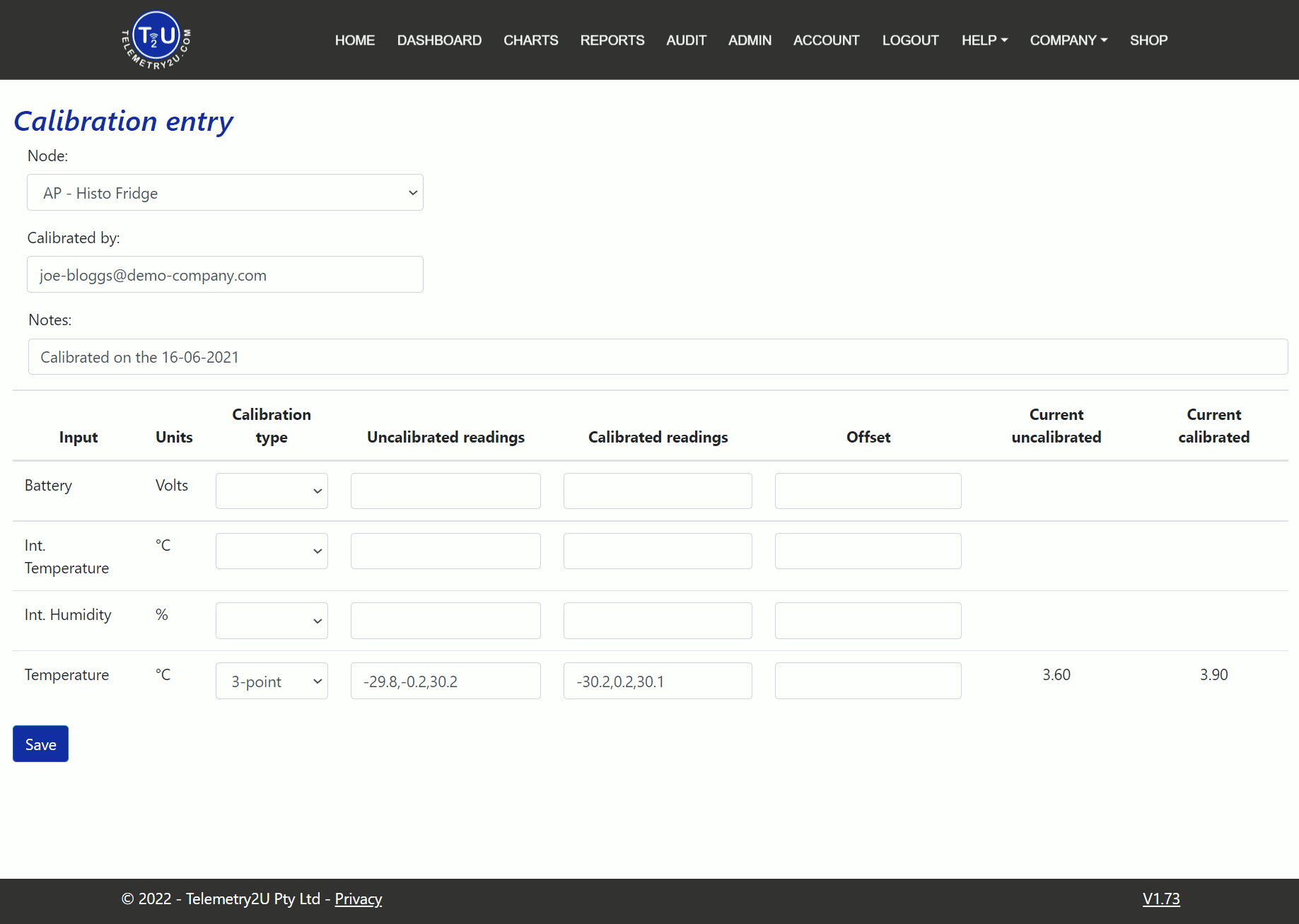
When you click on the Calibrate End-Devices link, you'll be taken to the Calibration Entry page. First, select the Node from the list that contains the sensor input you want to calibrate. The node will be added to a table at the bottom of the page, listing all sensor inputs available for calibration. The following options are available:
- Input - Shows all the inputs available for calibration on the selected node.
- Units - Displays the unit for each sensor input. These cannot be changed here.
- Calibration Type - Select either 2-point or 3-point calibration.
- Uncalibrated Readings - Enter raw sensor values separated by commas.
- Calibrated Readings - Enter reference sensor values separated by commas.
- Offset - Apply an offset to any calibration method.
- Current Uncalibrated - Displays sensor values without calibration coefficients.
- Current Calibrated - Shows sensor values with calibration applied to see the effect.
The Calibrated by field automatically populates with the user's email, but it can be changed. The Notes field is required and cannot be left blank. Click Save when done.
Note:
If a sensor doesn’t appear in the list, ensure it hasn’t been disabled under the Input Labels section on the Node Maintenance page. See Section 6.42 for details.
The image above shows an example of a 3-point calibration on the external temperature input of a Dragino LHT65. The LHT65 was placed in a water bath with a reference meter at -30°C, 0°C, and 30°C. The LHT65 readings (-29.8, -0.2, 30.2) were entered as Uncalibrated readings. The reference meter values (-30.2, 0.2, 30.1) were entered as Calibrated readings. No offset was applied. The Current uncalibrated and Current calibrated readings differ by 0.3, showing the calibration improved the accuracy by 0.3°C.
To apply only an offset without a full calibration, select 2-point calibration and enter "0,1" in both Uncalibrated readings and Calibrated readings. Then, input the desired offset and save. The change can be verified by comparing Current uncalibrated and Current calibrated readings.
Related Link:
For more detailed instructions, check out the Nata Facility Calibration Instructions for temperature sensors.
6.6.2 - Uploading Calibration Certificates
If you have a sensor with a calibration certificate, you can upload it to Telemetry2U for review and download by users with the View Certificates role.
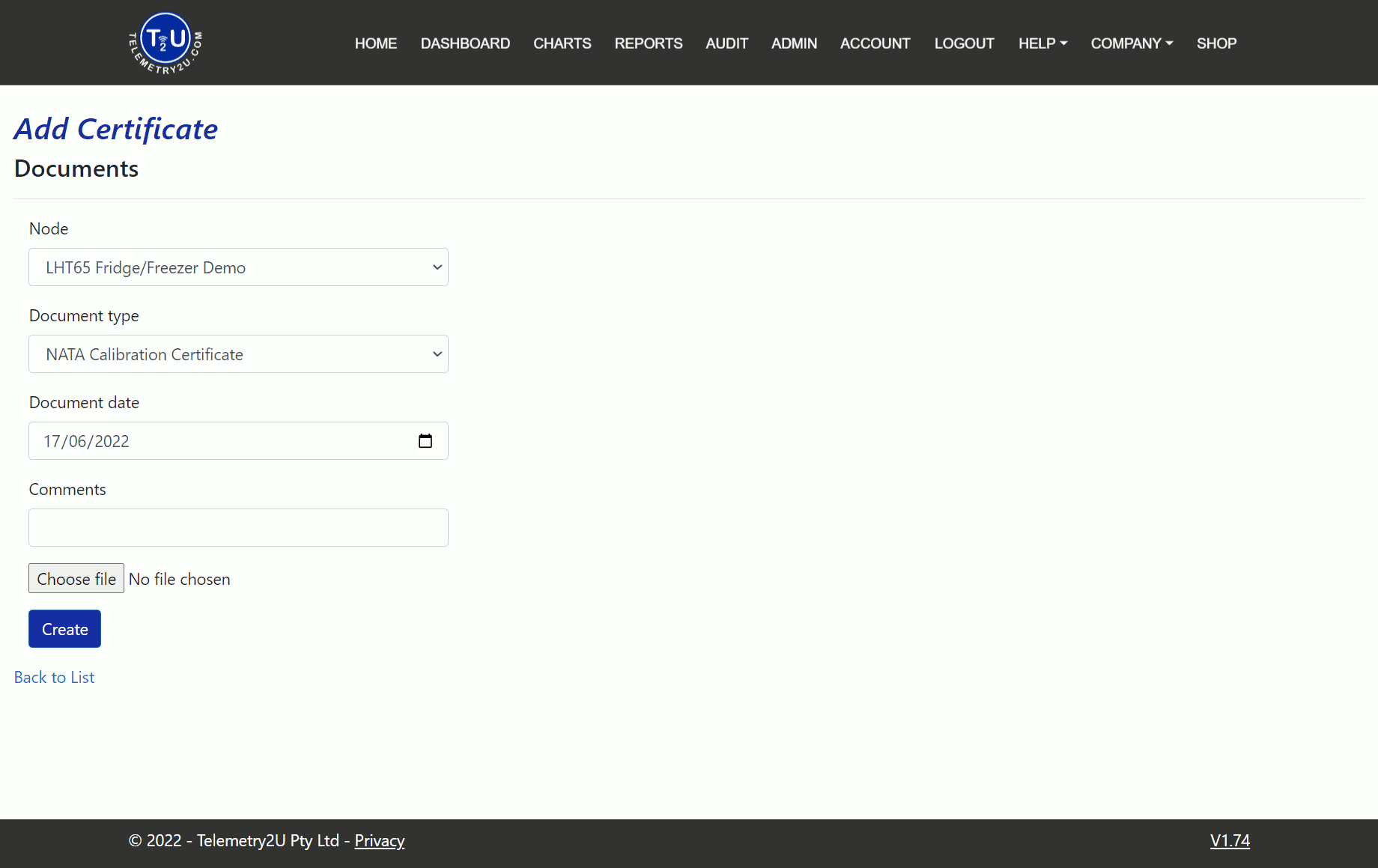
To upload a calibration certificate, click the Upload Calibration Certificate link under the Device Calibrations tab in the side menu. This will take you to the Documents Index page, where all nodes and their corresponding calibration certificates are listed. Click the Create new link at the top of the page to open the Add Certificate page. You will need to complete the following fields:
- Node – Select the node from the list to attach the calibration certificate to.
- Document Type – Select the type of document you are uploading.
- Document Date – Enter the date of the calibration certificate (usually the calibration date, not the upload date).
- Comments – Optional field for any calibration notes.
- Choose File – Select the PDF file from your local folders to upload.
Note:
Any user with the View Documents role can download calibration certificates, but they will not be able to upload or edit them.
6.6.3 - Downloading Calibration Certificates
If a calibration certificate has been uploaded, it can be reviewed and downloaded by users with either the Calibration role or the View Certificates role.
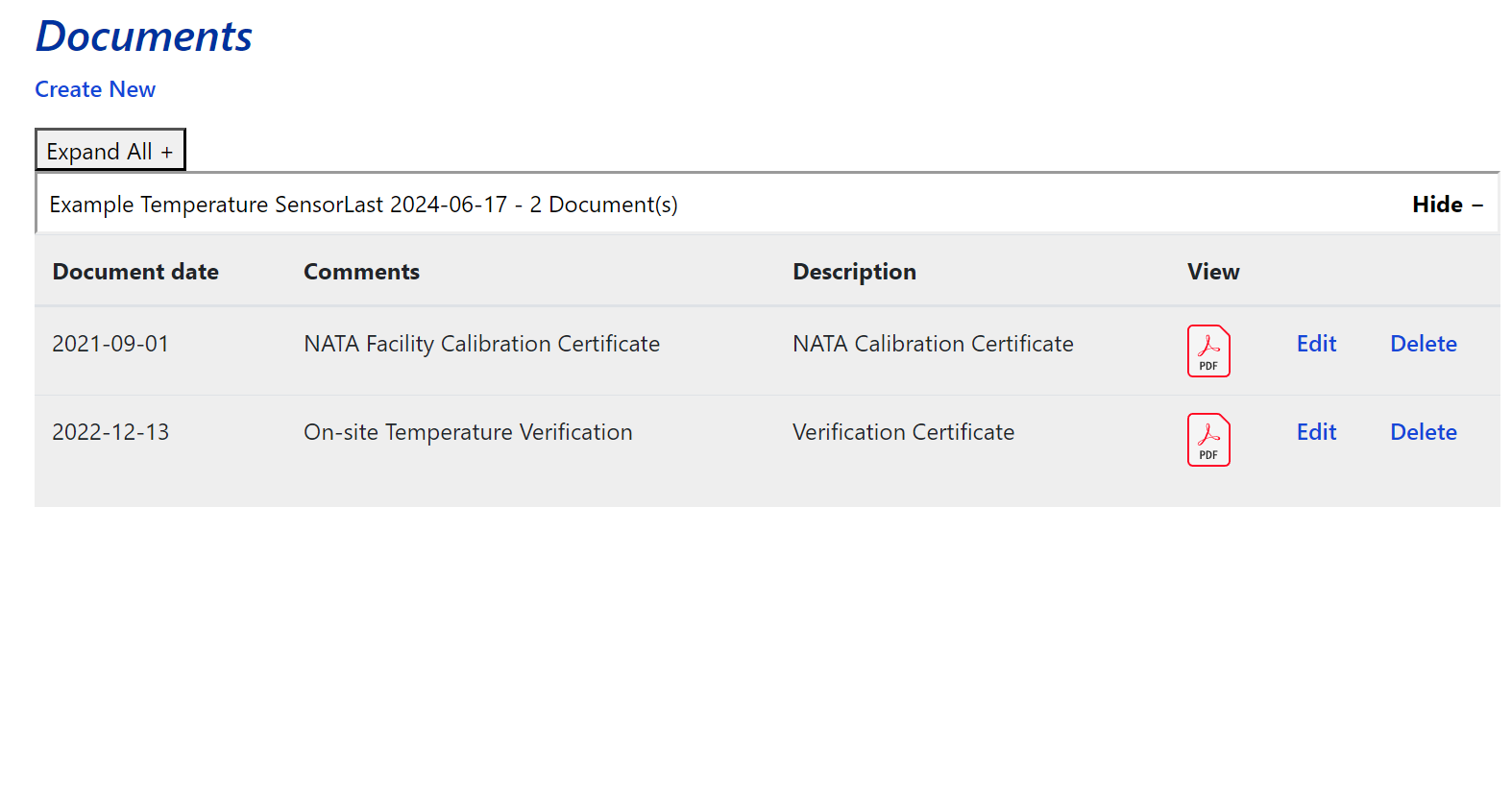
To download a calibration certificate, click the Upload Calibration Certificate link under the Device Calibrations tab in the side menu. This will take you to the Documents Index page, where all end-devices are listed in a table. If a device has an attached certificate, a View link will appear next to it. Clicking this will expand the row. You can also click the Expand all + button at the top of the page to expand all rows.
When a row is expanded, the following details are displayed:
- Documents Date – The date the calibration certificate was uploaded.
- Comments – A comment left by the user who uploaded the certificate.
- Description – A description of the calibration.
- View – Click the PDF icon to download the calibration certificate.
- Edit – Edit the calibration entry details.
- Delete – Remove the calibration certificate.
Note:
Users with this View Certificates role alone cannot upload or edit certificates; for that, they need the Calibrations role. There is no advantage to assigning the View Certificates role if the user has already been granted the Calibration role. Users with the Calibration role can perform all tasks.
6.7 - Actions and Automation
Users with the Action role can access both the Add / Edit Actions and Triggers and Create Action Schedule links under the Alerts and Actions tab in the side menu. Action groups consist of downlink commands sent to nodes to change settings or toggle outputs. These groups can be triggered by alert conditions (see section 6.3.1) or set up on a time-based schedule (see section 6.7.3). These features provide automation, allowing device outputs to be triggered based on sensor readings.
When you click on the Add / Edit Actions and Trigger link under the Action Maintenance section in the side menu, you'll be taken to the Action Index page when you can see a list of all actions already configured under your account. On the right side of each row, you’ll find options to Edit or Delete a specific action group.
To add a new Action Group gateway, click the Create New Action Group button at the top of the page. The form for adding a new action group is the same as the one used for editing an existing action group.
Note:
Actions created by a user with the Actions Admin role included in alert conditions as described in section 6.3.1
6.7.1 - Creating and Editing Actions
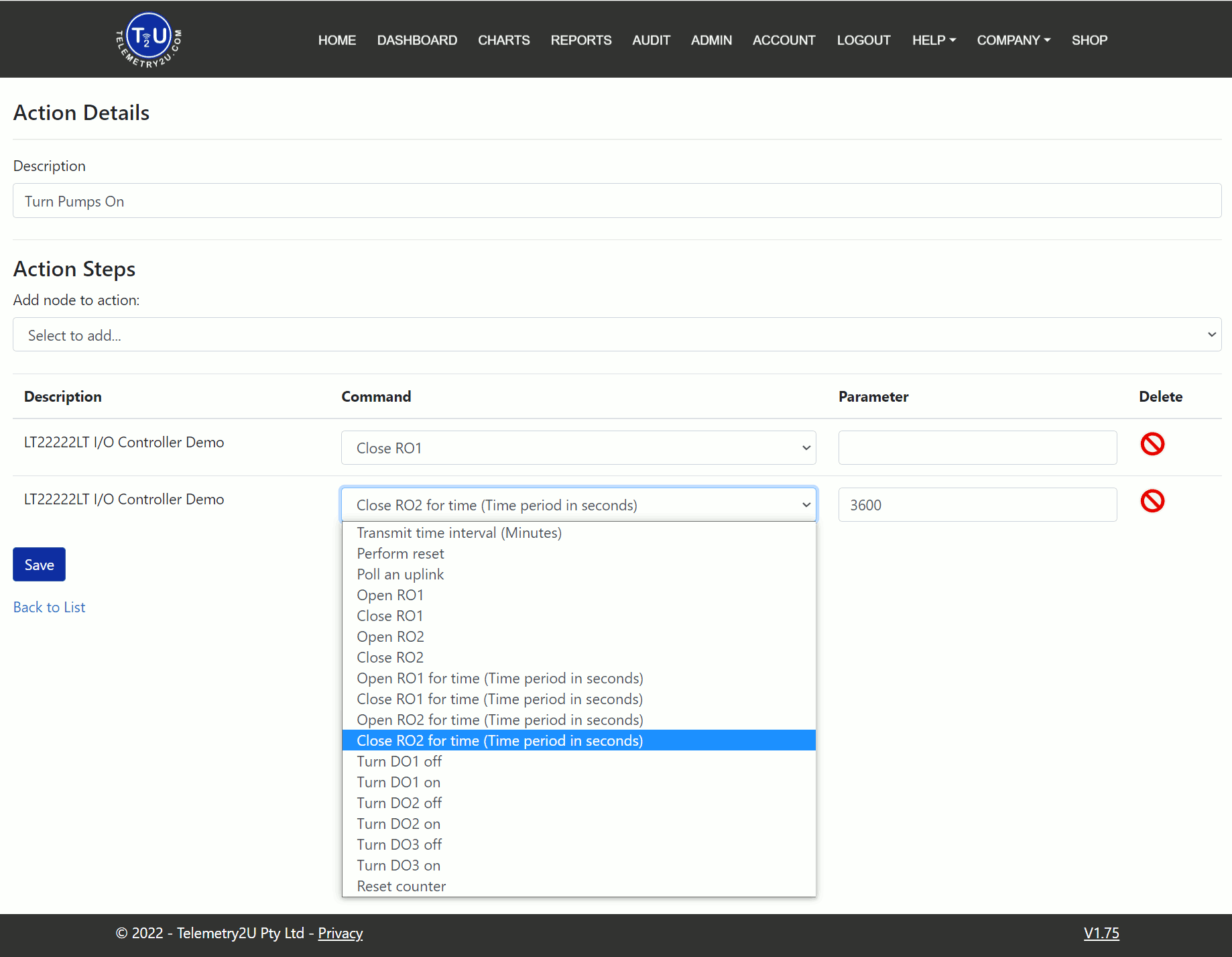
When you click the Add a New Action Group button or Edit an existing action group, you will be taken to a new page with a form divided into two sections:
- Description - Provide a unique name for the action group to identify it on all pages and lists.
- Add Node to Action - Select a node from the dropdown list to add it to the command table at the bottom of the page.
Once a node is added to the command table, configure the command settings with the following fields:
- Command - Choose the command to include. The list of available commands will depend on the Device Type.
- Parameter - Some commands require a variable, such as setting the transmit time. Enter it here, or leave blank if not needed.
- Delete - Click this button to remove a command from the list.
After making any changes, click the Save button at the bottom of the page.
Related Link:
You can add as many Action Steps as required. They will be sent in order as soon as the action is triggered by an alert condition or schedule.If you are using Class-A devices, the commands will be received after the next uplink as per the LoRaWAN protocol.
6.7.2 - Scheduling Actions
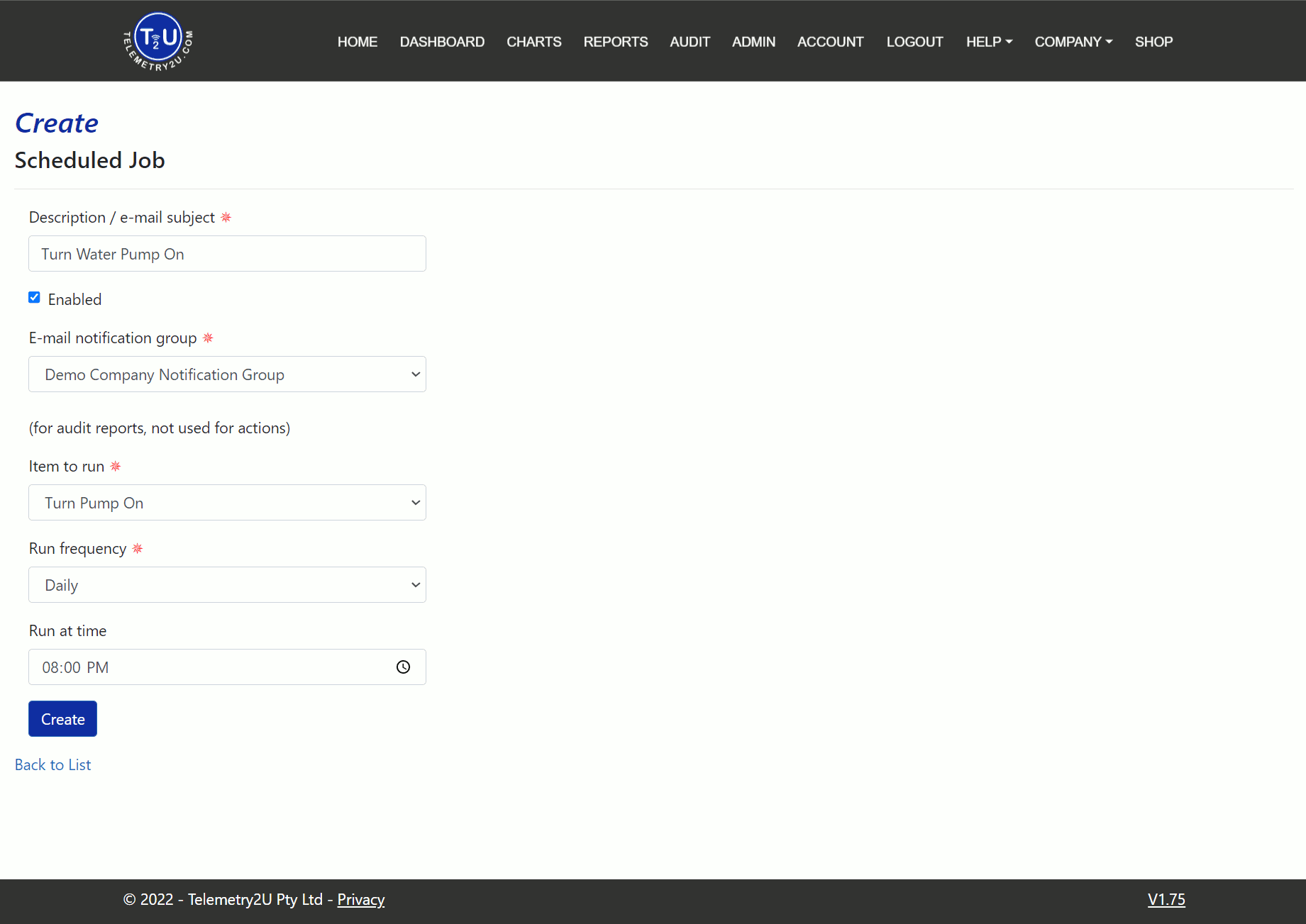
Once an action group is created, it can be added to a time-based schedule. Click the Create Action Schedule link under the Alerts and Actions tab in the side menu. This opens a page with a form to complete, including the following fields:
- Description / Email Subject – A name to identify the scheduled job on the main index page.
- Email Notification Group – Not used for running actions, only for audit reports.
- Item to Run – Select the action group to schedule from the dropdown list.
- Run Frequency – Choose how often to run the action group (daily, weekly, monthly, etc.).
- Run On – Select the specific day to run the action group.
- Run At Time – Pick the time you want the action group to run.
Make sure the Enabled checkbox is checked for the schedule to be active. Click the Create button at the bottom of the page after making any changes.
6.7.3 - Automating Actions
Actions can be triggered directly from alert conditions, allowing you to automate tasks based on sensor inputs, such as turning off a pump when the water level drops too low.
When configuring an alert condition (see Section 6.3.1 – Creating and Editing Alerts), you will have options for an Alert Action and a Recovery Action. These fields will display a list of any actions created as described in Section 6.7.1.
When a sensor input enters an alert state, the Alert Action is triggered, and the downlink commands in the action group are added to the downlink queue. These will be processed by the end-devices at the first opportunity, depending on the device class. When the sensor input recovers from the alert state, the Recovery Action is triggered in the same way.
Related Link:
Check out our step-by-step guide on automating tasks with actions in Telemetry2U at TB04 - LoRaWAN/IoT Automation Example.
6.8 - Integrations
Users with the Gateway Admin role will have access to the Setup Integration link under the Gateway and Network tab in the side menu.
Only users with the Gateway admin role will have the ability to add or edit an integration.
Integrations allow public LoRaWAN network servers to transfer raw data packets to and the application server, where you can visualize data, configure alerts, and more.
The main advantage of using an integration is that you may not need to invest in a gateway, assuming you're within range of a public LoRaWAN network.
When using an integration, it’s important that the node's Network Provider setting matches the integration type. You can read more about this in Section 6.4.1 – Creating and Editing Nodes. Multiple integrations for different network servers can be created, with the integration type used for the device determined by the Network Provider setting.
To create an integration, click on the Setup Integration link. Select the desired integration from the Network Provider dropdown box. If you've previously set up an integration, you’ll be taken directly to that page.
Note:
Public networks can be less stable than private LoRaWAN networks. If you need full control over your network, consider investing in a gateway. It may take up to an hour for an integration to start working, depending on the public network server used.
6.8.1 - Integrating to the Helium Network
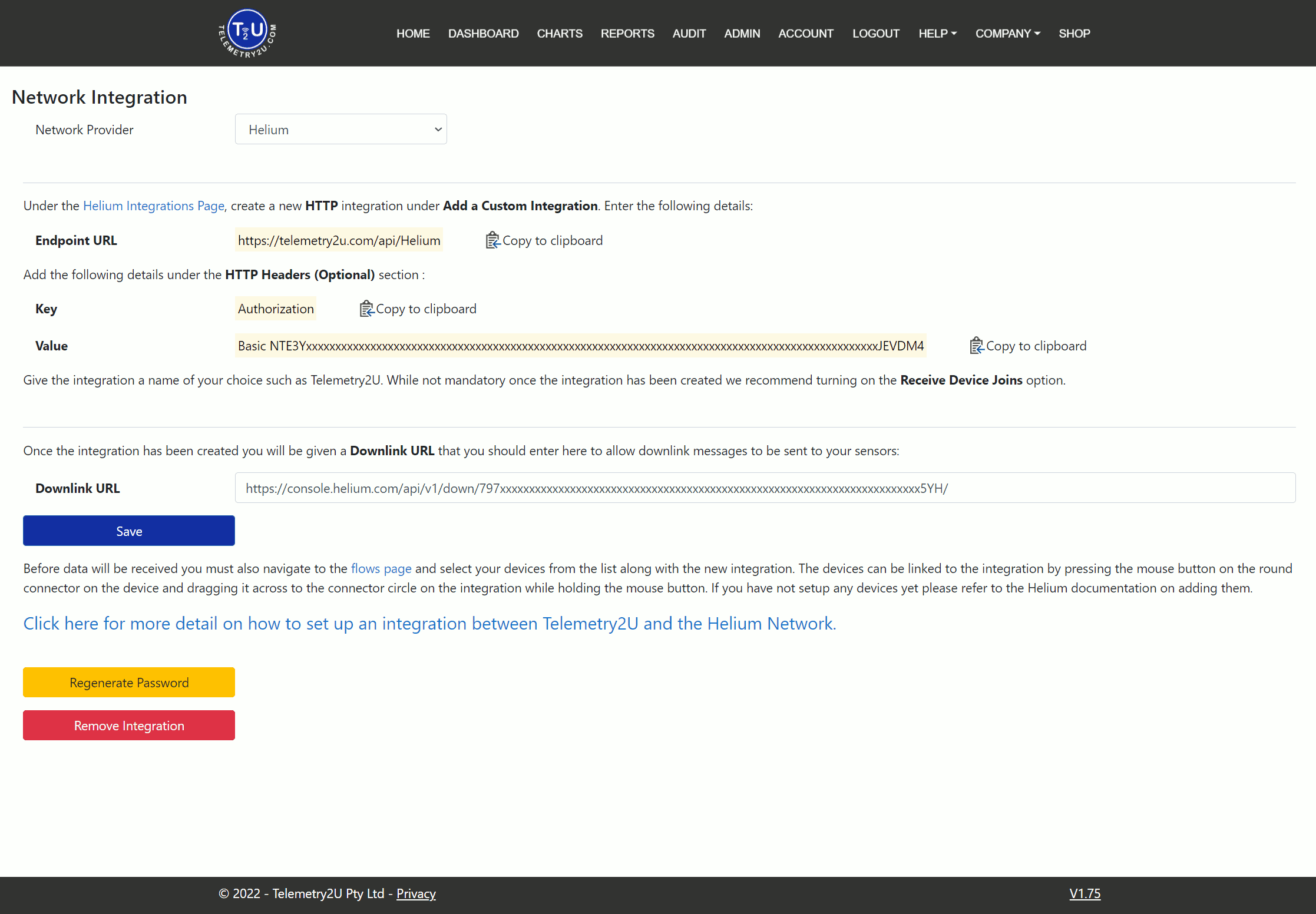
If you select Helium as the Network Provider, you'll be taken to the Helium Integration settings page. There are two main steps to the integration:
First, log in to your Helium account and create a new custom HTTP integration. Then, copy and paste the following details into the relevant sections on the Helium Console:
- Endpoint URL - This will always be https://telemetry2u.com/api/Helium.
- Key - This will always be Authorization.
- Value - This will be unique each time and can be reset using the button at the bottom of the page.
After saving the integration, stay on the Helium Console and return to the integration settings to find the Downlink URL. Copy that URL into the Downlink URL section in the Telemetry2U integration settings.
Click the Save button after making any changes.
You can generate a new Value using the Regenerate Password button or delete the integration from Telemetry2U using the Remove Integration button.
Related Link:
Check out our step-by-step guide for integrating with the Helium Network in TB03 - Integrating to the Helium Network
6.8.2 - Integrating to The Things Industries
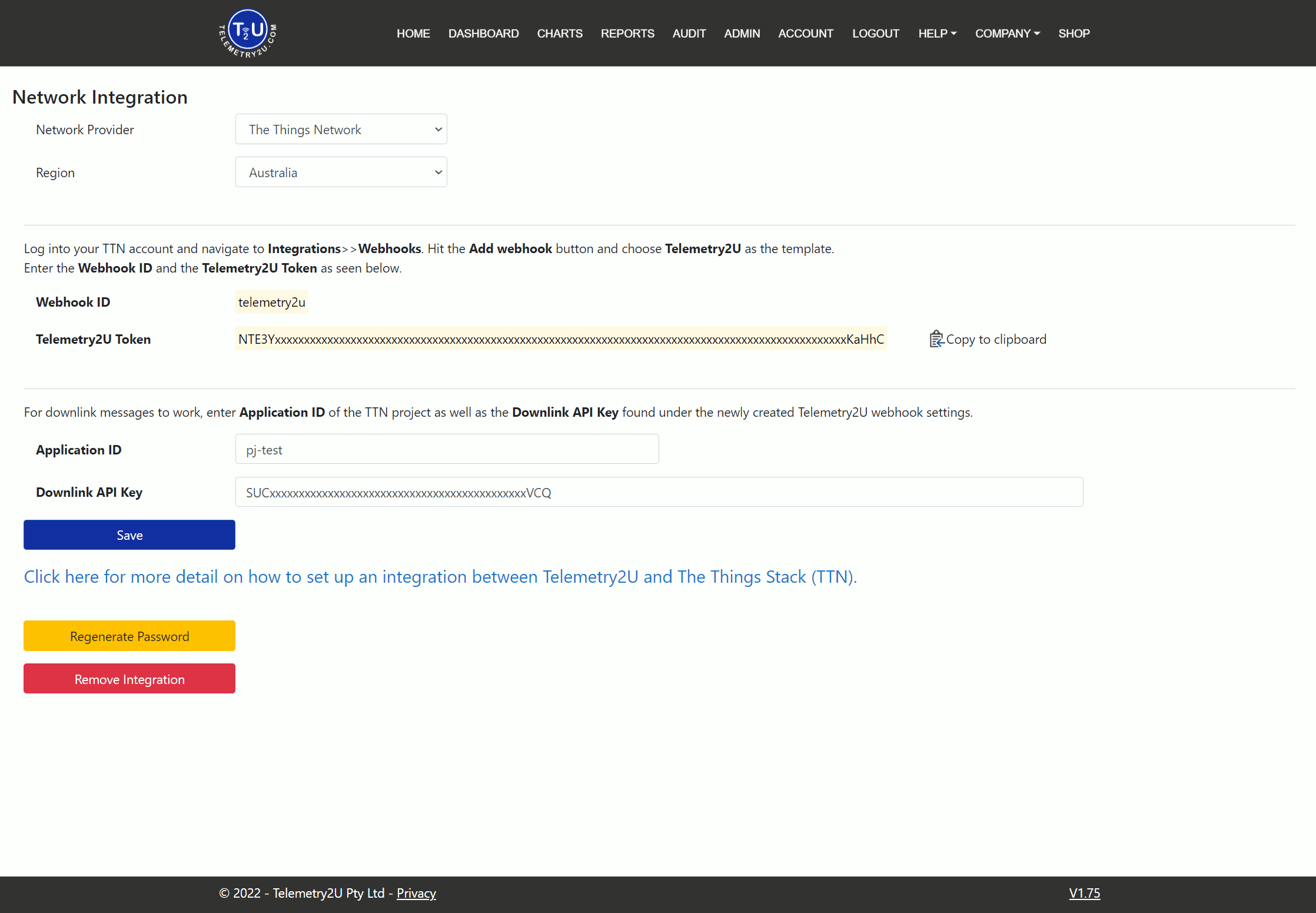
If you select TTN as the Network Provider, you’ll be taken to the TTN Integration settings page. First, select the appropriate Region from the dropdown box. Then log into your TTI account and add a new Webhook integration. Enter the following details into the respective fields:
- Webhook ID - This will always be Telemetry2U.
- Telemetry2U Token - This is unique each time and can be reset using the button at the bottom of the page.
After saving the integration, stay on the TTI Console and return to the integration settings. Copy the following back to the Telemetry2U integration page:
- Application ID - As configured on the TTI Console.
- Telemetry2U Token - A unique key required for downlink commands.
Click the Save button after making any changes.
You can generate a new Telemetry2U Token using the Regenerate Password button or delete the integration from Telemetry2U using the Remove Integration button.
Related Link:
Check out the step-by-step guide for integrating with TTI in their documentation.
6.9 - System Administration
Users with the Company Admin role will have access to the System Administrator tab in the side menu.
6.9.1 - Adding and Editing System Notices
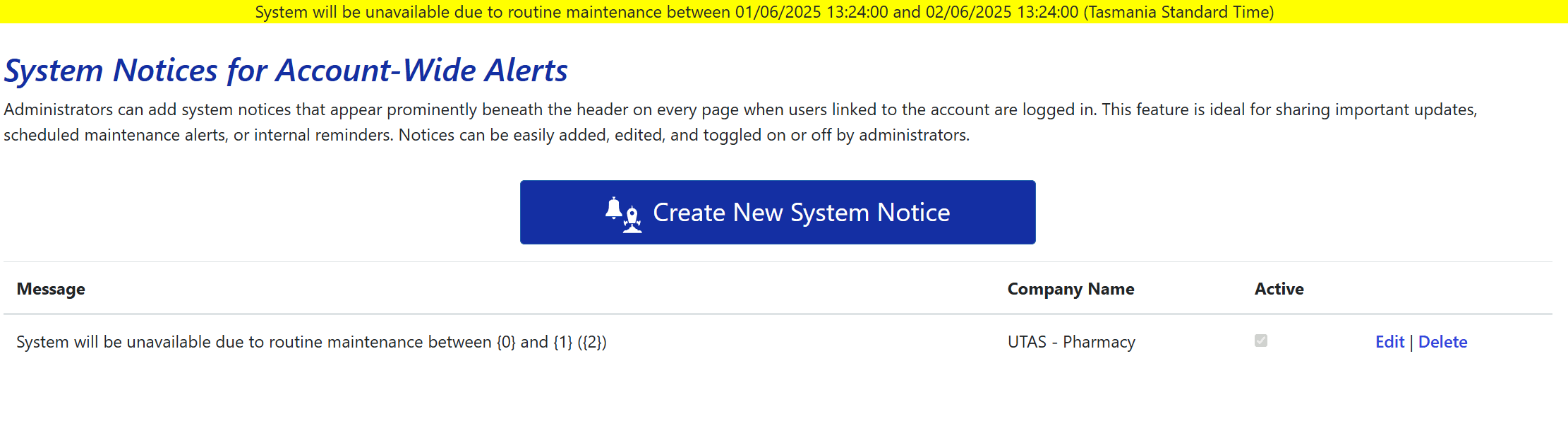
System Notices enable administrators to display important messages across the entire account. Once activated, these notices appear at the top of every page for all users linked to the account, directly beneath the main header. This feature is ideal for communicating scheduled maintenance alerts, service interruptions, policy updates, or general account-wide information.
When you click on the System Messages link under the System Administration section in the side menu, you’ll be taken to the System Messages index page where you can see a list of all existing system notices configured under your account. On the right side of each row, you’ll find options to Edit or Delete a specific system notice.
To add a new system notice, click the Create New System Notice button at the top of the page. The form for creating a new notice is the same as the one used to edit an existing notice.
Adding a New System Notice
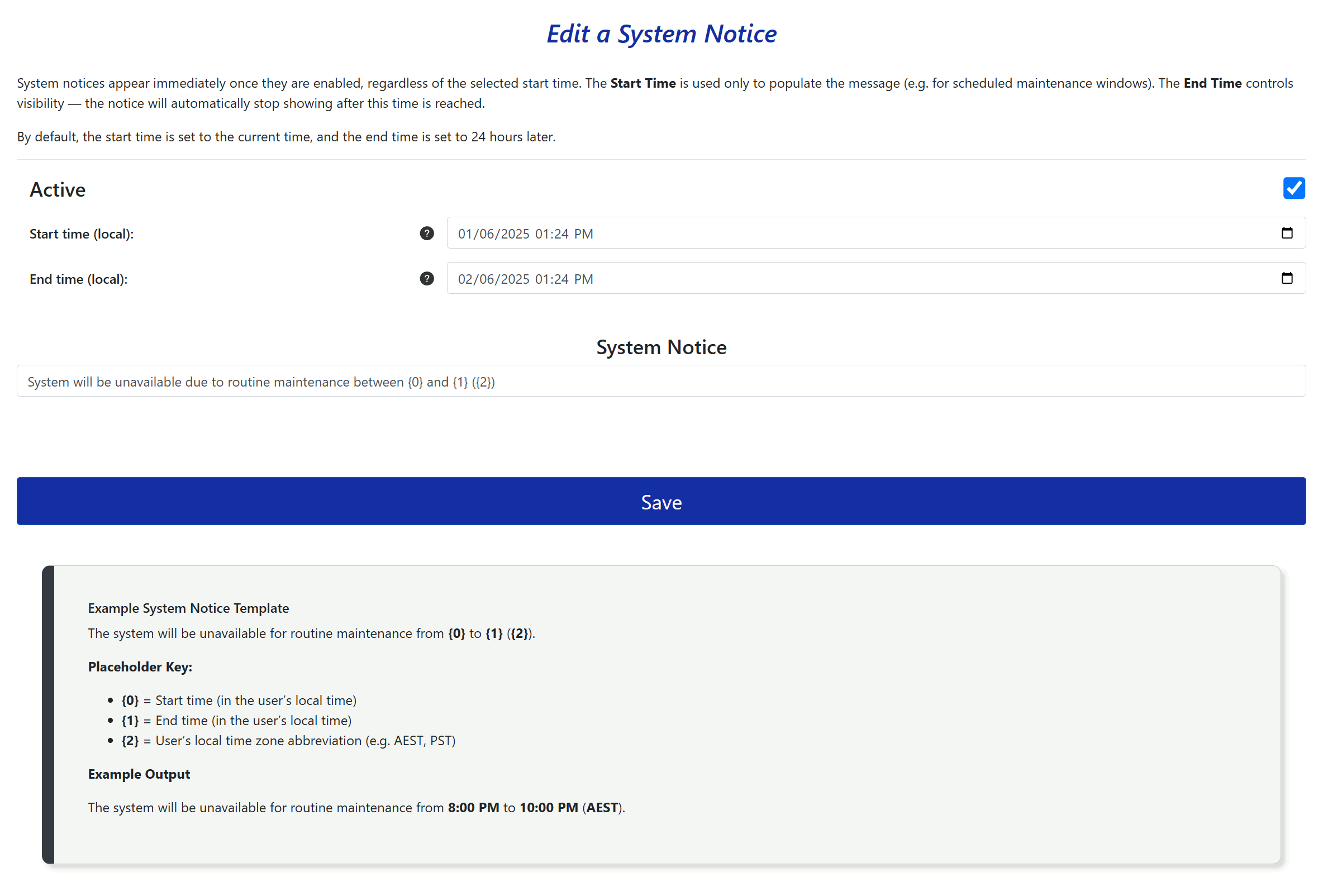
To add a new notice, navigate to the System Messages section under the Administration menu and click Create New System Notice. You will be prompted to enter the following details:
- Active: Toggle this switch to enable or disable the notice. Once enabled, the notice will appear immediately, regardless of the scheduled times.
- Start Time: This is used to populate the
{0}placeholder in your message. It does not control when the message appears. The value is converted and displayed in each user’s local time zone. - End Time: This serves two purposes: it fills the
{1}placeholder and determines when the notice stops displaying. The system notice will automatically disappear after the end time is reached. This time is also shown in each user’s local time zone. - Message: Enter the system notice message. You may use the placeholders
{0},{1}, and{2}to dynamically include the start time, end time, and the user’s local time zone abbreviation (e.g. AEST, PST).
Message Template and Placeholders
Customize your message using the following placeholders:
{0}– Start time (in the user's local time zone){1}– End time (in the user's local time zone){2}– Time zone abbreviation (e.g. AEST, PST)
Example Message
The system will be unavailable for routine maintenance from {0} to {1} ({2}).
Example Output
The system will be unavailable for routine maintenance from 8:00 PM to 10:00 PM (AEST).
Related Link:
Important Behavior Notes
- System notices are displayed immediately once the Active toggle is enabled.
- The Start Time is for display purposes only and does not delay the message display.
- The End Time controls when the notice stops displaying; the notice will automatically disappear after this time is reached.
- By default, new messages use the current time as the start time and 24 hours later as the end time.